Recognition of gout in rheumatoid arthritis: A case report
- PMID: 30558013
- PMCID: PMC6319970
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013540
Recognition of gout in rheumatoid arthritis: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and gout are common rheumatic diseases. However, their coexistance has been rarely reported. Here in, we describe a case of a middle aged Chinese woman having RA complicated with atypical gout on both the knee joints.
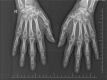
Patient concerns: A 44-year-old Chinese woman complained of swelling and tenderness of multiple joints since 10 months. She had a positive rheumatoid factor and high titers of anti-CCP antibody. She was diagnosed with RA, and commenced on methotrexate, leflunomide, and methylprednisolone. Her symptoms of pain and swelling over interphalangeal and wrists joints subsided except the knee joints. She was started with treat to target treatment (TTT) for RA and rest of her medications was adjusted accordingly. Surprisingly, her symptoms did not improve ever after the addition of a biologic agent, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α receptor antagonist.
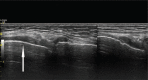
Diagnosis: Presence of urate crystals in the synovium was viewed under polarization microscope which was extracted from one of the knee joint. Hence, we established the diagnosis of RA complicated with gout.
Interventions: We commenced her on TNF-α receptor antagonist, colchicines, and febuxostat.
Outcomes: Her symptoms of pain and swelling improved significantly on both the knees and no longer recurred.
Lessons: Coexistence of RA and gout has been rarely reported as it is not frequently seen in clinical practice. Hence, when patients with RA with oligoarthritis repeatedly do not respond to TTT, a standard antirheumatism treatment, the possibility of RA complicating with gout should be rule out.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concomitant atypical knee gout and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Aug 6;12(22):5245-5252. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.5245. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39109047 Free PMC article.
-
Rare copresent rheumatoid arthritis and gout: comparison with pure rheumatoid arthritis and a literature review.Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Feb;27(2):231-5. doi: 10.1007/s10067-007-0771-2. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Clin Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18064397 Review.
-
Coexistent rheumatoid arthritis and gout: a case series and review of the literature.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Dec;36(12):2835-2838. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3856-6. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 29022182
-
Coexistence of chronic tophaceous gout and rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 1981 Nov-Dec;8(6):989-92. J Rheumatol. 1981. PMID: 7328573
-
The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis.Eur J Radiol. 1998 May;27 Suppl 1:S18-24. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(98)00038-2. Eur J Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9652497 Review.
Cited by
-
Concomitant atypical knee gout and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Aug 6;12(22):5245-5252. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.5245. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39109047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Houri LE, Watad A, Whitby A, et al. Coexistence of ischemic heart disease and rheumatoid arthritis patients—a case control study. Autoimmun Rev 2016;15:393–6. - PubMed
-
- Kuo CF, Grainge MJ, Zhang W, et al. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2015;11:649–62. - PubMed
-
- Kuo CF, Tsai WP, Liou LB. Rare copresent rheumatoid arthritis and gout: comparison with pure rheumatoid arthritis and a literature review. Clin Rheumatol 2008;27:231–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

