Posture-Specific Breathing Detection
- PMID: 30558319
- PMCID: PMC6308544
- DOI: 10.3390/s18124443
Posture-Specific Breathing Detection
Abstract
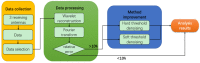
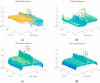
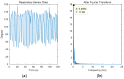
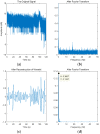
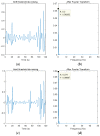
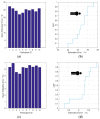
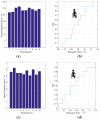
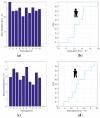
Human respiratory activity parameters are important indicators of vital signs. Most respiratory activity detection methods are naïve abd simple and use invasive detection technology. Non-invasive breathing detection methods are the solution to these limitations. In this research, we propose a non-invasive breathing activity detection method based on C-band sensing. Traditional non-invasive detection methods require special hardware facilities that cannot be used in ordinary environments. Based on this, a multi-input, multi-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM) system based on 802.11n protocol is proposed in this paper. Our system improves the traditional data processing method and has stronger robustness and lower bit relative error. The system detects the respiratory activity of different body postures, captures and analyses the information, and determines the influence of different body postures on human respiratory activity.
Keywords: body postures; non-invasive; respiratory activity detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lu G., Wang J., Yue Y., Jing X. Study of the Ballistocardiogram signal in life detection system based on radar; Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; Lyon, France. 22–26 August 2007. - PubMed
-
- Jing J. Study of the Design of Radar Life Detector Based on DSP Signal Processing System. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014;543:1009–1012. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.543-547.1009. - DOI
-
- Liang X., Zhang H., Lyu T., Xu L., Cao C., Gulliver T.A. Ultra-wide band impulse radar for life detection using wavelet packetdecomposition. Phys. Commun. 2018;29:31–47. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2018.04.004. - DOI
-
- Liang X., Lv T., Zhang H., Gao Y., Fang G. Through-wall human being detection using UWB impulse radar. Eurasip J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2018;1 doi: 10.1186/s13638-018-1054-0. - DOI
-
- Zhen Z., Liu F. Application of Wavelet Analysis Technique in the Life Sign Detection below Solid Material. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012;534:114–117.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

