Removal Effect of Atrazine in Co-Solution with Bisphenol A or Humic Acid by Different Activated Carbons
- PMID: 30558368
- PMCID: PMC6316426
- DOI: 10.3390/ma11122558
Removal Effect of Atrazine in Co-Solution with Bisphenol A or Humic Acid by Different Activated Carbons
Abstract
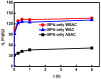
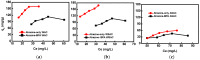
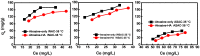
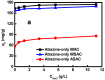
Activated carbons (ACs) based on apricot shells (AS), wood (W), and walnut shells (WS) were applied to adsorb atrazine in co-solutions. To study the effect of Bisphenol A (BPA) on the adsorption behavior of atrazine, the adsorption performance of ACs for BPA in single solution was studied. The results demonstrated that the adsorption kinetics of BPA fitted the pseudo-second-order model, the adsorption isotherms of BPA followed the Langmuir model. Meanwhile, the adsorption kinetics of atrazine fitted the pseudo-second-order kinetics model and the isotherm was consistent with the Freundlich model both in single solution and co-solution. In addition, competitive adsorption was observed when atrazine coexisted with BPA or humic acid. For the adsorption capacity, the adsorption amount of ASAC, WAC, and WSAC for atrazine obviously decreased by 18.0%, 30.0%, and 30.3% in the presence of BPA, respectively, which was due to the π-π interactions, hydrophobic interactions, and H-bonds, resulting in the competitive adsorption between atrazine and BPA. This study contributes to the further understanding of the adsorption behavior for atrazine in co-solution.
Keywords: NaCl; activated carbon; adsorption; atrazine; bisphenol A; co-solution; humic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Porous activated carbons derived from waste Moroccan pine cones for high-performance adsorption of bisphenol A from water.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 16;10(9):e29645. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29645. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38699018 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced removal of the endocrine disruptor compound Bisphenol A by adsorption onto green-carbon materials. Effect of real effluents on the adsorption process.J Environ Manage. 2020 Jul 15;266:110604. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110604. Epub 2020 Apr 17. J Environ Manage. 2020. PMID: 32310125
-
Decontamination of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by graphene adsorption.Langmuir. 2012 Jun 5;28(22):8418-25. doi: 10.1021/la301476p. Epub 2012 May 18. Langmuir. 2012. PMID: 22571829
-
[Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of atrazine on three types of humic acid].Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2010 Oct;30(10):2641-5. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2010. PMID: 21137390 Chinese.
-
Adsorption performance of modified agricultural waste materials for removal of emerging micro-contaminant bisphenol A: A comprehensive review.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Aug 1;780:146629. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146629. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 34030339 Review.
Cited by
-
Competitive adsorption of naphthalene and phenanthrene on walnut shell based activated carbon and the verification via theoretical calculation.RSC Adv. 2020 Mar 13;10(18):10703-10714. doi: 10.1039/c9ra09447d. eCollection 2020 Mar 11. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35492953 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Gaseous Ammonia Emissions Using Date Palm Pits Based Granular Activated Carbon.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Feb 27;17(5):1519. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051519. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32120871 Free PMC article.
-
On the Suitability of Almond Shells for the Manufacture of a Natural Low-Cost Bioadsorbent to Remove Brilliant Green: Kinetics and Equilibrium Isotherms Study.ScientificWorldJournal. 2021 Jan 29;2021:6659902. doi: 10.1155/2021/6659902. eCollection 2021. ScientificWorldJournal. 2021. PMID: 33603573 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

