First-in-Human Studies of [18F] Fluorohydroxyphenethylguanidines
- PMID: 30558502
- PMCID: PMC6424133
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.118.007965
First-in-Human Studies of [18F] Fluorohydroxyphenethylguanidines
Abstract
Background: Disease-induced damage to cardiac autonomic nerve populations is associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. The extent of cardiac sympathetic denervation, assessed using planar scintigraphy or positron emission tomography, has been shown to predict the risk of arrhythmic events in heart failure patients staged for implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy. The goal of this study was to perform first-in-human evaluations of 4-[18F]fluoro-meta-hydroxyphenethylguanidine and 3-[18F]fluoro-para-hydroxyphenethylguanidine, 2 new positron emission tomography radiotracers developed for quantifying regional cardiac sympathetic nerve density.
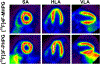
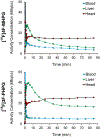
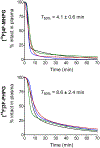
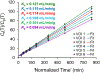
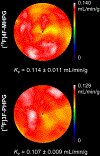
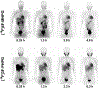
Methods and results: Cardiac positron emission tomography studies with 4-[18F]fluoro-meta-hydroxyphenethylguanidine and 3-[18F]fluoro-para-hydroxyphenethylguanidine were performed in normal subjects (n=4 each) to assess their imaging properties and organ kinetics. Patlak graphical analysis of their myocardial kinetics was evaluated as a technique for generating nerve density metrics. Whole-body biodistribution studies (n=4 each) were acquired and used to calculate human radiation dosimetry estimates. Patlak analysis proved to be an effective approach for quantifying regional nerve density. Using 960 left ventricular volumes of interest, across-subject Patlak slopes averaged 0.107±0.010 mL/min per gram for 4-[18F]fluoro-meta-hydroxyphenethylguanidine and 0.116±0.010 mL/min per gram for 3-[18F]fluoro-para-hydroxyphenethylguanidine. Tracer uptake was highest in heart, liver, kidneys, and salivary glands. Urinary excretion was the main elimination pathway.
Conclusions: 4-[18F]fluoro-meta-hydroxyphenethylguanidine and 3-[18F]fluoro-para-hydroxyphenethylguanidine each produce high-quality positron emission tomography images of the distribution of sympathetic nerves in human heart. Patlak analysis provides reproducible measurements of regional cardiac sympathetic nerve density at high spatial resolution. Further studies of these tracers in heart failure patients will be performed to identify the best agent for clinical development.
Clinical trial registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov . Unique identifier: NCT02385877.
Keywords: defibrillator; heart failure; positron-emission tomography; sympathetic nervous system.
Figures
Comment in
-
Imaging of Myocardial Catecholamine Uptake.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Dec;11(12):e008534. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.118.008534. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018. PMID: 30558497 No abstract available.
References
-
- Merlet P, Benvenuti C, Moyse D, Pouillart F, Dubois-Randé J-L, Duval A-M, Loisance D, Castaigne A, Syrota A. Prognostic value of MIBG imaging in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:917–923. - PubMed
-
- Nagahara D, Nakata T, Hashimoto A, Wakabayashi T, Kyuma M, Noda R, Shimoshige S, Uno K, Tsuchihashi K, Shimamoto K. Predicting the need for an implantable cardioverter defibrillator using cardiac metaiodobenzylguanidine activity together with plasma natriuretic peptide concentration or left ventricular function. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:225–233 - PubMed
-
- Kasama S, Toyama T, Sumino H, Nakazawa M, Matsumoto N, Sato Y, Kumakura H, Takayama Y, Ichikawa S, Suzuki T, Kurabayashi M. Prognostic value of serial 123I-MIBG imaging in patients with stabilized chronic heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:907–914. - PubMed
-
- Boogers MJ, Borleffs CJ, Henneman MM, van Bommel RJ, van Ramshorst J, Boersma E, Dibbets-Schneider P, Stokkel MP, van der Wall EE, Schalij MJ, Bax JJ. Cardiac sympathetic denervation assessed with 123I-iodine metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging predicts ventricular arrythmias in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:2769–2777. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson AF, Senior R, Cerqueira MD, Wong ND, Thomas GS, Lopez VA, Agostini D, Weiland F, Chandna H, Narula J. Myocardial iodine-123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine imaging and cardiac events in heart failure: results of the prospective ADMIRE-HF (AdreView Myocardial Imaging for Risk Evaluation in Heart Failure) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:2212–2221 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

