Novel compound heterozygous ATP6V1B1 mutations in a Chinese child patient with primary distal renal tubular acidosis: a case report
- PMID: 30558562
- PMCID: PMC6297984
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-018-1173-1
Novel compound heterozygous ATP6V1B1 mutations in a Chinese child patient with primary distal renal tubular acidosis: a case report
Abstract
Background: Distal renal tubular acidosis (dRTA) is a heterogeneous disorder characterized by normal anion gap metabolic acidosis. Autosomal recessive dRTA is usually caused by mutations occurring in ATP6V1B1 and ATP6V0A4 genes,encoding subunits B1 and a4 of apical H+-ATPase, respectively. The heterogeneous clinical manifestations of dRTA have been described in different ethnic groups harboring distinct mutations. Most of the reported cases are from Europe and Africa. At present, the prevalence of primary dRTA is still poorly elucidated in Chinese population.
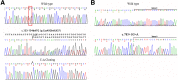
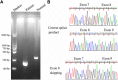
Case presentation: A 2-year and six-month-old female patient was hospitalized because of recurrent hypokalemia, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis and growth retardation. Laboratory investigations presented a normal anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, hypokalemia, and inappropriate alkaline urine. Renal ultrasound indicated bilateral nephrocalcinosis. Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) was confirmed with moderately severe (45 dB) on the left ear and severe (80 dB) on the right ear, which was accompanied with enlarged vestibular aqueduct (EVA) on both sides. According to these findings, a diagnosis of dRTA was made. To identify the pathogenic gene mutation, all coding regions of ATP6V1B1 and ATP6V0A4 gene, including intron-exon boundaries, were analyzed using PCR followed by direct sequence analysis. The splicing variants were verified in peripheral blood leucocytes of the patient by RT-PCR. As a result, two novel heterozygous mutations in ATP6V1B1 were identified in the child. One mutation was a successive 2-nucleotide deletion in exon 2(c.133-134delTG), which caused a marked nonsense mediated mRNA decay. The other was a guanine to adenine substitution of the first nucleotide of intron 8(c.785 + 1 G > A), which led to the exclusion of exon 8. After treatment with sodium citrate, potassium citrateand citric acid, metabolic acidosis and hypokalemia were corrected, but her hearing decreased gradually during the 2 years and had to accept the use of bilateral hearing aids.
Conclusions: We described two novel dRTA associated mutations in ATP6V1B1 identified in a Chinese child patient accompanying with SNHL and EVA. Our study will help to expand the understanding of this rare disease in Chinese population.
Keywords: ATP6V1B1 gene; Distal renal tubular acidosis; Enlarged vestibular aqueduct; Sensorineural hearing loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Additional analyses were approved by the Ethics Committee of the affiliated hospital of Qingdao University (No. 20170211).Informed consent to participate and publish was obtained from guardians of the subject.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the guardians of the patient for publication of this Case Report and any accompanying images. The A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular diagnosis of distal renal tubular acidosis in Tunisian patients: proposed algorithm for Northern Africa populations for the ATP6V1B1, ATP6V0A4 and SCL4A1 genes.BMC Med Genet. 2013 Nov 20;14:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-14-119. BMC Med Genet. 2013. PMID: 24252324 Free PMC article.
-
ATP6V1B1 recurrent mutations in Algerian deaf patients associated with renal tubular acidosis.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Feb;129:109772. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109772. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31733597
-
Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of inherited distal renal tubular acidosis.J Nephrol. 2018 Aug;31(4):511-522. doi: 10.1007/s40620-017-0447-1. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 28994037 Review.
-
Homozygous and compound heterozygous mutations in the ATP6V1B1 gene in patients with renal tubular acidosis and sensorineural hearing loss.Clin Genet. 2013 Mar;83(3):274-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2012.01891.x. Epub 2012 May 11. Clin Genet. 2013. PMID: 22509993
-
[Primary distal renal tubular acidosis].Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2009 Mar-Apr;67(2):135-40. doi: 10.1684/abc.2009.0307. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2009. PMID: 19297287 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Genetic Determinants of Non-Syndromic Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct: A Review.Audiol Res. 2021 Aug 28;11(3):423-442. doi: 10.3390/audiolres11030040. Audiol Res. 2021. PMID: 34562878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Karet FE, Finberg KE, Nelson RD, Nayir A, Mocan H, Sanjad SA, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Santos F, Cremers CW, Di Pietro A, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding B1 subunit of H+-ATPase cause renal tubular acidosis with sensorineural deafness. Nat Genet. 1999;21(1):84–90. doi: 10.1038/5022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bouzidi H, Daudon M, Najjar MF. Primary distal renal tubular acidosis. Ann Biol Clin. 2009;67(2):135–140. - PubMed
-
- Elhayek D, Perez de Nanclares G, Chouchane S, Hamami S, Mlika A, Troudi M, Leban N, Ben Romdane W, Gueddiche MN, El Amri F, et al. Molecular diagnosis of distal renal tubular acidosis in Tunisian patients: proposed algorithm for northern Africa populations for the ATP6V1B1, ATP6V0A4 and SCL4A1 genes. BMC Med Genet. 2013;14:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-14-119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

