FBP21's C-Terminal Domain Remains Dynamic When Wrapped around the c-Sec63 Unit of Brr2 Helicase
- PMID: 30558886
- PMCID: PMC6372199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.11.3123
FBP21's C-Terminal Domain Remains Dynamic When Wrapped around the c-Sec63 Unit of Brr2 Helicase
Abstract
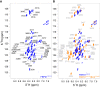
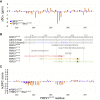
Based on our recent finding that FBP21 regulates human Brr2 helicase activity involved in the activation of the spliceosomal B-complex, we investigated the structural and dynamic contribution of FBP21 to the interaction. By using NMR spectroscopy, we could show that the 50 C-terminal residues of FBP21 (FBP21326-376), which are sufficient to fully form the interaction with the C-terminal Sec63 unit of Brr2 (Brr2C-Sec63), adopt a random-coil conformation in their unbound state. Upon interaction with Brr2C-Sec63, 42 residues of FBP21326-376 cover the large binding site on Brr2C-Sec63 in an extended conformation. Short charged motifs are steering complex formation, still allowing the bound state to retain dynamics. Based on fragment docking in combination with experimental restraints, we present models of the complex structure. The FBP21326-376/Brr2C-Sec63 interaction thus presents an example of an intrinsically disordered protein/ordered-protein interaction in which a large binding site provides high specificity and, in combination with conformational disorder, displays a relatively high affinity.
Copyright © 2018 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Dyson H.J., Wright P.E. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005;6:197–208. - PubMed
-
- Tompa P., Fuxreiter M. Fuzzy complexes: polymorphism and structural disorder in protein-protein interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008;33:2–8. - PubMed
-
- Tompa P. Intrinsically unstructured proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002;27:527–533. - PubMed
-
- Gunasekaran K., Tsai C.J., Nussinov R. Extended disordered proteins: targeting function with less scaffold. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003;28:81–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

