Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children with Obesity
- PMID: 30559024
- PMCID: PMC6440815
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.11.021
Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children with Obesity
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in children with obesity because current estimates range from 1.7% to 85%. A second objective was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) for NAFLD in children with obesity.
Study design: We evaluated children aged 9-17 years with obesity for the presence of NAFLD. Diseases other than NAFLD were excluded by history and laboratories. Hepatic steatosis was measured by liver magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction. The diagnostic accuracy of ALT for detecting NAFLD was evaluated.
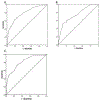
Results: The study included 408 children with obesity that had a mean age of 13.2 years and mean body mass index percentile of 98.0. The study population had a mean ALT of 32 U/L and median hepatic magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction of 3.7%. The estimated prevalence of NAFLD was 26.0% (95% CI 24.2%-27.7%), 29.4% in male patients (CI 26.1%-32.7%) and 22.6% in female patients (CI 16.0%-29.1%). Optimal ALT cut-point was 42 U/L (47.8% sensitivity, 93.2% specificity) for male and 30 U/L (52.1% sensitivity, 88.8% specificity) for female patients. The classification and regression tree model with sex, ALT, and insulin had 80% diagnostic accuracy for NAFLD.
Conclusions: NAFLD is common in children with obesity, but NAFLD and obesity are not concomitant. In children with obesity, NAFLD is present in nearly one-third of boys and one-fourth of girls.
Keywords: BMI; NAFLD; pediatric.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Claude B. Sirlin, MD has industry research support from Bayer, GE, Philips and Siemens; consults for AMRA, Boehringer and Guerbet; is on the speaker’s bureau for Resoundant and has lab service agreements with Gilead, ICON, Intercept, Shire and Synageva.
Figures
Comment in
-
Virtual Reality: New Insights Regarding the Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents with Obesity Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging.J Pediatr. 2019 Apr;207:8-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.12.025. J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30922506 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schwimmer JB, Deutsch R, Kahen T, Lavine JE, Stanley C, Behling C. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:1388–1393. - PubMed
-
- Doycheva I, Issa D, Watt KD, Lopez R, Rifai G, Alkhouri N. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis is the Most Rapidly Increasing Indication for Liver Transplantation in Young Adults in the United States. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2018; 52:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Vos MB, Abrams SH, Barlow SE, Caprio S, Daniels SR, Kohil R, et al. NASPGHAN Clinical Practice Guildeline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease In Children: Recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017; 64:319–334. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

