Effects of Molidustat in the Treatment of Anemia in CKD
- PMID: 30559105
- PMCID: PMC6364546
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.02510218
Effects of Molidustat in the Treatment of Anemia in CKD
Erratum in
-
Correction.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Oct 7;14(10):1524. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08610719. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31444173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and objectives: The efficacy and safety of molidustat, a hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, have been evaluated in three 16-week, phase 2b studies in patients with CKD and anemia who are not on dialysis (DaIly orAL treatment increasing endOGenoUs Erythropoietin [DIALOGUE] 1 and 2) and in those who are on dialysis (DIALOGUE 4).
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: DIALOGUE 1 was a placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trial (25, 50, and 75 mg once daily; 25 and 50 mg twice daily). DIALOGUE 2 and 4 were open-label, variable-dose trials, in which treatment was switched from darbepoetin (DIAGLOGUE 2) or epoetin (DIALOGUE 4) to molidustat or continued with the original agents. Starting molidustat ranged between 25-75 and 25-150 mg daily in DIAGLOGUE 2 and 4, respectively, and could be titrated to maintain hemoglobin levels within predefined target ranges. The primary end point was the change in hemoglobin level between baseline and the mean value from the last 4 weeks of the treatment period.
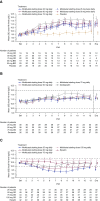
Results: In DIAGLOGUE 1 (n=121), molidustat treatment was associated with estimated increases in mean hemoglobin levels of 1.4-2.0 g/dl. In DIAGLOGUE 2 (n=124), hemoglobin levels were maintained within the target range after switching to molidustat, with an estimated difference in mean change in hemoglobin levels between molidustat and darbepoetin treatments of up to 0.6 g/dl. In DIAGLOGUE 4 (n=199), hemoglobin levels were maintained within the target range after switching to molidustat 75 and 150 mg, with estimated differences in mean change between molidustat and epoetin treatment of -0.1 and 0.4 g/dl. Molidustat was generally well tolerated, and most adverse events were mild or moderate in severity.
Conclusions: The overall phase 2 efficacy and safety profile of molidustat in patients with CKD and anemia enables the progression of its development into phase 3.
Keywords: Darbepoetin alfa; EPO protein; Epoetin Alfa; Humans; Prolyl Hydroxylases; Prolyl-Hydroxylase Inhibitors; Pyrazoles; Renal Insufficiency, Chronic; Triazoles; anemia; chronic kidney disease; erythropoietin; hemoglobin; human; hypoxia; molidustat; renal dialysis.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



References
-
- Culleton BF, Manns BJ, Zhang J, Tonelli M, Klarenbach S, Hemmelgarn BR: Impact of anemia on hospitalization and mortality in older adults. Blood 107: 3841–3846, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Hsu CY, McCulloch CE, Curhan GC: Epidemiology of anemia associated with chronic renal insufficiency among adults in the United States: Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 504–510, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Astor BC, Muntner P, Levin A, Eustace JA, Coresh J: Association of kidney function with anemia: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988-1994). Arch Intern Med 162: 1401–1408, 2002 - PubMed
-
- El-Achkar TM, Ohmit SE, McCullough PA, Crook ED, Brown WW, Grimm R, Bakris GL, Keane WF, Flack JM; Kidney Early Evaluation Program : Higher prevalence of anemia with diabetes mellitus in moderate kidney insufficiency: The Kidney Early Evaluation Program. Kidney Int 67: 1483–1488, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

