AKT/mTORC2 Inhibition Activates FOXO1 Function in CLL Cells Reducing B-Cell Receptor-Mediated Survival
- PMID: 30559170
- PMCID: PMC6398589
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2036
AKT/mTORC2 Inhibition Activates FOXO1 Function in CLL Cells Reducing B-Cell Receptor-Mediated Survival
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether inhibition of mTOR kinase-mediated signaling represents a valid therapeutic approach for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Experimental design: Stratification of mTOR activity was carried out in patients with primary CLL samples and an aggressive CLL-like mouse model. The potency of dual mTOR inhibitor AZD8055 to induce apoptosis in primary CLL cells was assessed in the presence/absence of B-cell receptor (BCR) ligation. Furthermore, we addressed the molecular and functional impact of dual mTOR inhibition in combination with BTK inhibitor ibrutinib.
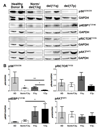
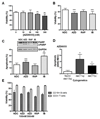
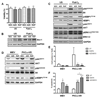
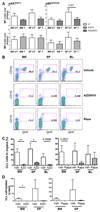
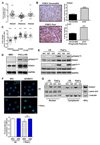
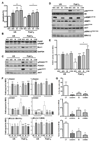
Results: Differential regulation of basal mTORC1 activity was observed in poor prognostic CLL samples, with elevated p4EBP1T37/46 and decreased p70S6 kinase activity, suggesting that dual mTORC1/2 inhibitors may exhibit improved response in poor prognostic CLL compared with rapalogs. AZD8055 treatment of primary CLL cells significantly reduced CLL survival in vitro compared with rapamycin, preferentially targeting poor prognostic subsets and overcoming BCR-mediated survival advantages. Furthermore, AZD8055, and clinical analog AZD2014, significantly reduced CLL tumor load in mice. AKT substrate FOXO1, while overexpressed in CLL cells of poor prognostic patients in LN biopsies, peripheral CLL cells, and mouse-derived CLL-like cells, appeared to be inactive. AZD8055 treatment partially reversed FOXO1 inactivation downstream of BCR crosslinking, significantly inhibiting FOXO1T24 phosphorylation in an mTORC2-AKT-dependent manner, to promote FOXO1 nuclear localization, activity, and FOXO1-mediated gene regulation. FOXO1 activity was further significantly enhanced on combining AZD8055 with ibrutinib.
Conclusions: Our studies demonstrate that dual mTOR inhibitors show promise as future CLL therapies, particularly in combination with ibrutinib.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
FoxO1/Rictor axis induces a nongenetic adaptation to ibrutinib via Akt activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 22;134(23):e173770. doi: 10.1172/JCI173770. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39436708 Free PMC article.
-
FoxO1-GAB1 axis regulates homing capacity and tonic AKT activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood. 2021 Sep 2;138(9):758-772. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020008101. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33786575 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CD38 Enhances the Antileukemic Activity of Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 1;25(13):3974-3985. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3412. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30940652 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Semin Oncol. 2016 Apr;43(2):251-9. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.02.008. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Semin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27040703 Review.
-
Discrete signaling mechanisms of mTORC1 and mTORC2: Connected yet apart in cellular and molecular aspects.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 May;64:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 28189457 Review.
Cited by
-
ACE Loss Drives Renal Cell Carcinoma Growth and Invasion by Modulating AKT-FOXO1.Biologics. 2024 Dec 19;18:397-412. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S485178. eCollection 2024. Biologics. 2024. PMID: 39717370 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR inhibition overcomes primary and acquired resistance to Wee1 inhibition by augmenting replication stress in epithelial ovarian cancers.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Mar 1;10(3):908-924. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32266099 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton tyrosine kinase covalent inhibition shapes the immune microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Haematologica. 2025 Aug 1;110(8):1758-1773. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2024.286663. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Haematologica. 2025. PMID: 40079085 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-196a increases apoptosis in B cells through downregulation of FOXO1.Mol Cells. 2025 Jul;48(7):100223. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2025.100223. Epub 2025 May 20. Mol Cells. 2025. PMID: 40403879 Free PMC article.
-
HBX-induced miR-5188 impairs FOXO1 to stimulate β-catenin nuclear translocation and promotes tumor stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma.Theranostics. 2019 Oct 12;9(25):7583-7598. doi: 10.7150/thno.37717. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31695788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zenz T, Mertens D, Küppers R, Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S. From pathogenesis to treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:37–50. - PubMed
-
- Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL, et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;94(6):1840–7. - PubMed
-
- Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;94(6):1848–54. - PubMed
-
- Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Barry TS, Wright G, Davis RE, Henrickson SE, et al. ZAP-70 expression identifies a chronic lymphocytic leukemia subtype with unmutated immunoglobulin genes, inferior clinical outcome, and distinct gene expression profile. Blood. 2003;101:4944–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

