Neurodevelopmental disease genes implicated by de novo mutation and copy number variation morbidity
- PMID: 30559488
- PMCID: PMC6309590
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0288-4
Neurodevelopmental disease genes implicated by de novo mutation and copy number variation morbidity
Abstract
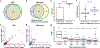
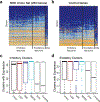
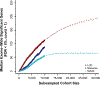
We combined de novo mutation (DNM) data from 10,927 individuals with developmental delay and autism to identify 253 candidate neurodevelopmental disease genes with an excess of missense and/or likely gene-disruptive (LGD) mutations. Of these genes, 124 reach exome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10-7) for DNM. Intersecting these results with copy number variation (CNV) morbidity data shows an enrichment for genomic disorder regions (30/253, likelihood ratio (LR) +1.85, P = 0.0017). We identify genes with an excess of missense DNMs overlapping deletion syndromes (for example, KIF1A and the 2q37 deletion) as well as duplication syndromes, such as recurrent MAPK3 missense mutations within the chromosome 16p11.2 duplication, recurrent CHD4 missense DNMs in the 12p13 duplication region, and recurrent WDFY4 missense DNMs in the 10q11.23 duplication region. Network analyses of genes showing an excess of DNMs highlights functional networks, including cell-specific enrichments in the D1+ and D2+ spiny neurons of the striatum.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
E.E.E. is on the scientific advisory board (SAB) of DNAnexus, Inc.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

