TRP Channels in Angiogenesis and Other Endothelial Functions
- PMID: 30559679
- PMCID: PMC6287032
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01731
TRP Channels in Angiogenesis and Other Endothelial Functions
Abstract
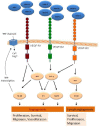
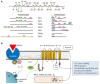
Angiogenesis is the growth of blood vessels mediated by proliferation, migration, and spatial organization of endothelial cells. This mechanism is regulated by a balance between stimulatory and inhibitory factors. Proangiogenic factors include a variety of VEGF family members, while thrombospondin and endostatin, among others, have been reported as suppressors of angiogenesis. Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels belong to a superfamily of cation-permeable channels that play a relevant role in a number of cellular functions mostly derived from their influence in intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis. Endothelial cells express a variety of TRP channels, including members of the TRPC, TRPV, TRPP, TRPA, and TRPM families, which play a relevant role in a number of functions, including endothelium-induced vasodilation, vascular permeability as well as sensing hemodynamic and chemical changes. Furthermore, TRP channels have been reported to play an important role in angiogenesis. This review summarizes the current knowledge and limitations concerning the involvement of particular TRP channels in growth factor-induced angiogenesis.
Keywords: TRP channels; TRPC; TRPM; TRPV; VEGF; angiogenesis; endothelial cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Significance of Transient Receptor Potential Channels in Vascular Function.In: Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 26. In: Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 26. PMID: 21204506 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Transient receptor potential channels and regulation of lung endothelial permeability.Pulm Circ. 2013 Dec;3(4):802-15. doi: 10.1086/674765. Pulm Circ. 2013. PMID: 25006396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRP channels and the control of vascular function.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;10(2):127-32. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.11.010. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20060363 Review.
-
Calcium-Permeable Channels in Tumor Vascularization: Peculiar Sensors of Microenvironmental Chemical and Physical Cues.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;182:111-137. doi: 10.1007/112_2020_32. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 32809072 Review.
-
Transient receptor potential channels in endothelium: solving the calcium entry puzzle?Endothelium. 2003;10(1):5-15. doi: 10.1080/10623320303356. Endothelium. 2003. PMID: 12699072 Review.
Cited by
-
The Molecular Heterogeneity of Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry in Vascular Endothelial Cells: The Different roles of Orai1 and TRPC1/TRPC4 Channels in the Transition from Ca2+-Selective to Non-Selective Cation Currents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 7;24(4):3259. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043259. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct and Overlapping Expression Patterns of the Homer Family of Scaffolding Proteins and Their Encoding Genes in Developing Murine Cephalic Tissues.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 13;21(4):1264. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041264. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32070057 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α-dependent upregulation of angiogenic factors by mechanical stimulation in retinal pigment epithelial cells.Dis Model Mech. 2024 Apr 1;17(4):dmm050640. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050640. Epub 2024 May 1. Dis Model Mech. 2024. PMID: 38691000 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing angiogenic efficacy of conditioned medium using light stimulation of human adipose-derived stem cells.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 13;5(1):957. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03838-3. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36100628 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Ca2+ Signaling, Angiogenesis and Vasculogenesis: just What It Takes to Make a Blood Vessel.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 14;20(16):3962. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163962. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31416282 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

