Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Outcome of Encephalitis in French Guiana
- PMID: 30560767
- PMCID: PMC6367637
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0308
Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Outcome of Encephalitis in French Guiana
Abstract
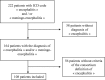
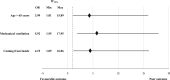
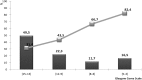
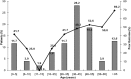
The aim of our study was to describe the clinical features, the etiologies, and the factors associated with poor outcome of encephalitis in French Guiana. Our study was retrospective, including all cases of encephalitis hospitalized in the Cayenne General Hospital, from January 2007 to July 2017. Patients were included through the 2013 encephalitis consortium criteria and the outcome was evaluated using the Glasgow outcome scale at 3 months from the diagnosis of encephalitis. We included 108 patients, giving an approximate incidence rate of four cases/100,000 inhabitants/year. The origin of the encephalitis was diagnosed in 81 cases (75%), and 72 of them (66.7%) were from an infectious origin. The most common infectious causes were Cryptococcus sp. (18.5%) independently of the immune status, Toxoplasma gondii (13.9%), and Streptococcus pneumoniae (5.5%). In the follow-up, 48 patients (46.6%) had poor outcome. Independent risk factors associated with poor outcome at 3 months were "coming from inside area of the region" (P = 0.036, odds ratio [OR] = 4.19; CI 95% = 1.09-16.06), need for mechanical ventilation (P = 0.002, OR = 5.92; CI 95% = 1.95-17.95), and age ≥ 65 years (P = 0.049, OR = 3.99; CI 95% = 1.01-15.89). The most identified cause of encephalitis in French Guiana was Cryptococcus. The shape of the local epidemiology highlights the original infectious situation with some local specific pathogens.
Figures
References
-
- Boucher A, Herrmann JL, Morand P, Buzelé R, Crabol Y, Stahl JP, Mailles A, 2017. Epidemiology of infectious encephalitis causes in 2016. Med Mal Infect 47: 221–235. - PubMed
-
- Glaser CA, et al. 2006. Beyond viruses: clinical profiles and etiologies associated with encephalitis. Clin Infect Dis 43: 1565–1577. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

