SCL/TAL1 cooperates with Polycomb RYBP-PRC1 to suppress alternative lineages in blood-fated cells
- PMID: 30560907
- PMCID: PMC6299140
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07787-6
SCL/TAL1 cooperates with Polycomb RYBP-PRC1 to suppress alternative lineages in blood-fated cells
Abstract
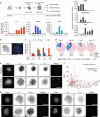
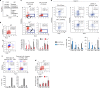
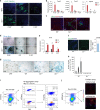
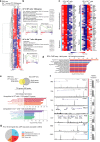
During development, it is unclear if lineage-fated cells derive from multilineage-primed progenitors and whether active mechanisms operate to restrict cell fate. Here we investigate how mesoderm specifies into blood-fated cells. We document temporally restricted co-expression of blood (Scl/Tal1), cardiac (Mesp1) and paraxial (Tbx6) lineage-affiliated transcription factors in single cells, at the onset of blood specification, supporting the existence of common progenitors. At the same time-restricted stage, absence of SCL results in expansion of cardiac/paraxial cell populations and increased cardiac/paraxial gene expression, suggesting active suppression of alternative fates. Indeed, SCL normally activates expression of co-repressor ETO2 and Polycomb-PRC1 subunits (RYBP, PCGF5) and maintains levels of Polycomb-associated histone marks (H2AK119ub/H3K27me3). Genome-wide analyses reveal ETO2 and RYBP co-occupy most SCL target genes, including cardiac/paraxial loci. Reduction of Eto2 or Rybp expression mimics Scl-null cardiac phenotype. Therefore, SCL-mediated transcriptional repression prevents mis-specification of blood-fated cells, establishing active repression as central to fate determination processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


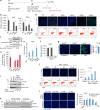

References
-
- Tam PP, Parameswaran M, Kinder SJ, Weinberger RP. The allocation of epiblast cells to the embryonic heart and other mesodermal lineages: the role of ingression and tissue movement during gastrulation. Development. 1997;124:1631–1642. - PubMed
-
- Kinder SJ, et al. The orderly allocation of mesodermal cells to the extraembryonic structures and the anteroposterior axis during gastrulation of the mouse embryo. Development. 1999;126:4691–4701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_UU_12009/9/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00016/9/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L008963/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0902418/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12009/11/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U137961146/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/S005382/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1000729/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00016/11/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900747/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

