Aquaporin-4-dependent glymphatic solute transport in the rodent brain
- PMID: 30561329
- PMCID: PMC6307855
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.40070
Aquaporin-4-dependent glymphatic solute transport in the rodent brain
Abstract
The glymphatic system is a brain-wide clearance pathway; its impairment contributes to the accumulation of amyloid-β. Influx of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) depends upon the expression and perivascular localization of the astroglial water channel aquaporin-4 (AQP4). Prompted by a recent failure to find an effect of Aqp4 knock-out (KO) on CSF and interstitial fluid (ISF) tracer transport, five groups re-examined the importance of AQP4 in glymphatic transport. We concur that CSF influx is higher in wild-type mice than in four different Aqp4 KO lines and in one line that lacks perivascular AQP4 (Snta1 KO). Meta-analysis of all studies demonstrated a significant decrease in tracer transport in KO mice and rats compared to controls. Meta-regression indicated that anesthesia, age, and tracer delivery explain the opposing results. We also report that intrastriatal injections suppress glymphatic function. This validates the role of AQP4 and shows that glymphatic studies must avoid the use of invasive procedures.
Keywords: aquaporin-4; cerebrospinal fluid; glymphatic; meta-analysis; mouse; neuroscience; replication study; solute transport.
© 2018, Mestre et al.
Conflict of interest statement
HM, LH, AX, WF, WZ, TP, HM, GM, RC, MS, MP, VP, TD, BK, XW, BP, AT, IL, YA, MY, JT, MX, HH, AA, JI, MN No competing interests declared
Figures

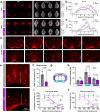
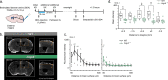
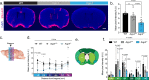
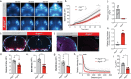


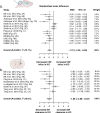
References
-
- Achariyar TM, Li B, Peng W, Verghese PB, Shi Y, McConnell E, Benraiss A, Kasper T, Song W, Takano T, Holtzman DM, Nedergaard M, Deane R. Glymphatic distribution of CSF-derived apoE into brain is isoform specific and suppressed during sleep deprivation. Molecular Neurodegeneration. 2016;11:74. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0138-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- AIBL Research Group. Rainey-Smith SR, Mazzucchelli GN, Villemagne VL, Brown BM, Porter T, Weinborn M, Bucks RS, Milicic L, Sohrabi HR, Taddei K, Ames D, Maruff P, Masters CL, Rowe CC, Salvado O, Martins RN, Laws SM. Genetic variation in Aquaporin-4 moderates the relationship between sleep and brain Aβ-amyloid burden. Translational Psychiatry. 2018;8:47. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0094-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Otsuka T, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Haug FM, Froehner SC, Adams ME, Neely JD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A. An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. PNAS. 2003;100:2106–2111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0437946100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arras M, Autenried P, Rettich A, Spaeni D, Rülicke T. Optimization of intraperitoneal injection anesthesia in mice: drugs, dosages, adverse effects, and anesthesia depth. Comparative Medicine. 2001;51:443–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 AG054093/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048769/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS100366/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- NS078394/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR002244/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HL089221/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS110049/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS089709/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS099371/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057575-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS089709/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054456/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG054456/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS100366/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS061800/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057575/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089221/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS099371/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- AG048769/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- NS061800/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

