FOXF2 is required for cochlear development in humans and mice
- PMID: 30561639
- PMCID: PMC6452198
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddy431
FOXF2 is required for cochlear development in humans and mice
Abstract
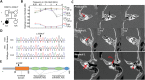
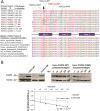
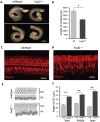
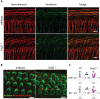
Molecular mechanisms governing the development of the human cochlea remain largely unknown. Through genome sequencing, we identified a homozygous FOXF2 variant c.325A>T (p.I109F) in a child with profound sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) associated with incomplete partition type I anomaly of the cochlea. This variant is not found in public databases or in over 1000 ethnicity-matched control individuals. I109 is a highly conserved residue in the forkhead box (Fox) domain of FOXF2, a member of the Fox protein family of transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes involved in embryogenic development as well as adult life. Our in vitro studies show that the half-life of mutant FOXF2 is reduced compared to that of wild type. Foxf2 is expressed in the cochlea of developing and adult mice. The mouse knockout of Foxf2 shows shortened and malformed cochleae, in addition to altered shape of hair cells with innervation and planar cell polarity defects. Expressions of Eya1 and Pax3, genes essential for cochlear development, are reduced in the cochleae of Foxf2 knockout mice. We conclude that FOXF2 plays a major role in cochlear development and its dysfunction leads to SNHL and developmental anomalies of the cochlea in humans and mice.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Morton C.C. and Nance W.E. (2006) Newborn hearing screening—a silent revolution. N. Engl. J. Med., 354, 2151–2164. - PubMed
-
- Jackler R.K., Luxford W.M. and House W.F. (1987) Congenital malformations of the inner ear: a classification based on embryogenesis. Laryngoscope, 97, 2–14. - PubMed
-
- Adibelli Z.H., Isayeva L., Koc A.M., Catli T., Adibelli H. and Olgun L. (2017) The new classification system for inner ear malformations: the INCAV system. Acta Otolaryngol., 137, 246–252. - PubMed
-
- Sennaroglu L. and Saatci I. (2002) A new classification for cochleovestibular malformations. Laryngoscope, 112, 2230–2241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

