Assessment of quality of life in pediatric patients with pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 30562156
- PMCID: PMC6607578
- DOI: 10.1177/2045894018822985
Assessment of quality of life in pediatric patients with pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
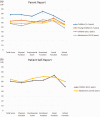
The aim of this study is to evaluate quality of life in four domains (physical, emotional, social, and school) in pediatric patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) using a validated survey (PedsQL). This is a prospective cohort study of pediatric patients aged 2-18 years with PH. Parents of all children and patients aged 8-18 years with appropriate developmental capacity completed the PedsQL survey in the clinic. Results were compared with published norms for pediatric patients, those with congenital heart disease (CHD) and cancer. Thirty-three children were enrolled yielding 32 parent and 18 patient self-reports: seven patients were aged 2-4 years; three were aged 5-7 years; 11 were aged 8-12 years, and 12 were aged 13-18 years. Twenty-one patients were classified as World Health Organization (WHO) Group I pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), 11 WHO Group III PH due to lung disease, and one WHO Group V with segmental PH. Thirteen patients were NYHA functional class (FC) 1, 12 were FC 2, eight were FC 3, and none were FC 4. The PH cohort had significantly lower scores than healthy children in all domains on both parent and self-report. The PH cohort also had significantly lower scores than patients with CHD (parent report: total, physical, social, school; patient self-report: total, physical, school) and cancer (parent report: school; patient self-report: physical, school). Close to 50% of participants reported at risk scores in each domain. The quality of life in pediatric PH patients assessed by PedsQL revealed functional impairment in multiple domains. Administration of the PedsQL during outpatient encounters may provide an easy, reproducible method to assess quality of life and direct referral for interventional services.
Keywords: functional ability/impairment/quality of life/physical activity; pediatric cardiovascular disease; pulmonary hypertension.
Figures

References
-
- D’Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, et al. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Ann Int Med 1991; 115: 343–349. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, McGoon MD, Elliott CG, et al. Survival in childhood pulmonary arterial hypertension: insights from the registry to evaluate early and long-term pulmonary arterial hypertension disease management. Circulation 2012; 125: 113–122. - PubMed
-
- Yung D, Widlitz AC, Rosenzweig EB, et al. Outcomes in children with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 2004; 110: 660–665. - PubMed
-
- Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 62: D34–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

