Atomic Structure of a Fluorescent Ag8 Cluster Templated by a Multistranded DNA Scaffold
- PMID: 30562465
- PMCID: PMC6606393
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b12203
Atomic Structure of a Fluorescent Ag8 Cluster Templated by a Multistranded DNA Scaffold
Abstract
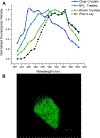
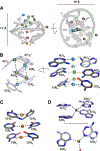
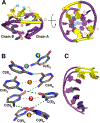
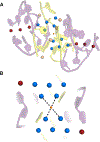
Multinuclear silver clusters encapsulated by DNA exhibit size-tunable emission spectra and rich photophysics, but their atomic organization is poorly understood. Herein, we describe the structure of one such hybrid chromophore, a green-emitting Ag8 cluster arranged in a Big Dipper-shape bound to the oligonucleotide A2C4. Three 3' cytosine metallo-base pairs stabilize a parallel A-form-like duplex with a 5' adenine-rich pocket, which binds a metallic, trapezoidal-shaped Ag5 moiety via Ag-N bonds to endo- and exocyclic nitrogens of cytosine and adenine. The unique DNA configuration, constrained coordination environment, and templated Ag8 cluster arrangement highlight the reciprocity between the silvers and DNA in adopting this structure. These first atomic details of a DNA-encapsulated Ag cluster fluorophore illuminate many aspects of biological assembly, nanoscience, and metal cluster photophysics.
Figures
References
-
- Kubo R, Electronic properties of metallic fine particles. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 1962, 17 (6), 975–986.
-
- Jin R, Atomically precise metal nanoclusters: stable sizes and optical properties. Nanoscale 2015, 7 (5), 1549–1565. - PubMed
-
- Peyser LA; Vinson AE; Bartko AP; Dickson RM, Photoactivated fluorescence from individual silver nanoclusters. Science 2001, 291 (5501), 103–106. - PubMed
-
- de Heer WA, The physics of simple metal clusters: experimental aspects and simple models. Rev. Mod. Phys 1993, 65 (3), 611–676.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

