Cytokine Networks Dysregulation during HTLV-1 Infection and Associated Diseases
- PMID: 30563084
- PMCID: PMC6315340
- DOI: 10.3390/v10120691
Cytokine Networks Dysregulation during HTLV-1 Infection and Associated Diseases
Abstract
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is the causative agent of a neural chronic inflammation, called HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) and of a malignant lymphoproliferation, called the adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL). The mechanisms through which the HTLV-1 induces these diseases are still unclear, but they might rely on immune alterations. HAM/TSP is associated with an impaired production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as IFN-γ, TNF-α, CXCL9, or CXCL10. ATLL is associated with high levels of IL-10 and TGF-β. These immunosuppressive cytokines could promote a protumoral micro-environment. Moreover, HTLV-1 infection impairs the IFN-I production and signaling, and favors the IL-2, IL-4, and IL-6 expression. This contributes both to immune escape and to infected cells proliferation. Here, we review the landscape of cytokine dysregulations induced by HTLV-1 infection and the role of these cytokines in the HTLV-1-associated diseases progression.
Keywords: ATLL; HAM/TSP; HTLV-1; cytokines; immune system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
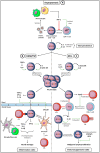
References
-
- Kannian P., Yin H., Doueiri R., Lairmore M.D., Fernandez S., Green P.L. Distinct Transformation Tropism Exhibited by Human T Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-2 Is the Result of Postinfection T Cell Clonal Expansion. J. Virol. 2012;86:3757–3766. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06900-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

