The Role of MicroRNAs in the Metastatic Process of High-Risk HPV-Induced Cancers
- PMID: 30563114
- PMCID: PMC6316057
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10120493
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Metastatic Process of High-Risk HPV-Induced Cancers
Abstract
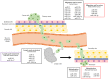
High-risk human papillomavirus (HPV)-driven cancers represent a major health concern worldwide. Despite the constant effort to develop and promote vaccination against HPVs, there is still a high percentage of non-vaccinated population. Furthermore, secondary prevention programs are not ubiquitous worldwide and not widely followed. Metastatic disease is the cause of the great majority of cancer-associated deaths, making it essential to determine its underlying mechanisms and to identify actionable anti-metastatic targets. Within certain types of cancer (e.g., head and neck), HPV-positive tumors show different dissemination patterns when compared with their HPV-negative counterparts, implicating HPV-related factors in the metastatic process. Among the many groups of biomolecules dysregulated by HPV, microRNAs have recently emerged as key regulators of carcinogenesis, able to control complex processes like cancer metastization. In this review, we present recent data on the role of microRNAs in the metastization of HPV-related cancers and on their possible clinical relevance as biomarkers of metastatic disease and/or as therapeutic targets.
Keywords: anogenital cancer; cervical cancer; head and neck cancer; high-risk HPV; invasion; metastization; microRNAs; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HPV: Molecular pathways and targets.Curr Probl Cancer. 2018 Mar-Apr;42(2):161-174. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Curr Probl Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29706467 Review.
-
Loss of Dependence on Continued Expression of the Human Papillomavirus 16 E7 Oncogene in Cervical Cancers and Precancerous Lesions Arising in Fanconi Anemia Pathway-Deficient Mice.mBio. 2016 May 17;7(3):e00628-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00628-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27190216 Free PMC article.
-
A novel, broad spectrum therapeutic HPV vaccine targeting the E7 proteins of HPV16, 18, 31, 45 and 52 that elicits potent E7-specific CD8T cell immunity and regression of large, established, E7-expressing TC-1 tumors.Vaccine. 2011 Oct 13;29(44):7857-66. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.07.090. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21816200
-
Combined Transcriptome and Proteome Analysis of Immortalized Human Keratinocytes Expressing Human Papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) Oncogenes Reveals Novel Key Factors and Networks in HPV-Induced Carcinogenesis.mSphere. 2019 Mar 27;4(2):e00129-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00129-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 30918060 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of human papillomavirus (HPV)-related tumors in people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017 Nov;15(11):987-999. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2017.1392854. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017. PMID: 29027811 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-18a targeting of the STK4/MST1 tumour suppressor is necessary for transformation in HPV positive cervical cancer.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Jun 18;16(6):e1008624. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008624. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32555725 Free PMC article.
-
The E6 and E7 proteins of beta3 human papillomavirus 49 can deregulate both cellular and extracellular vesicles-carried microRNAs.Infect Agent Cancer. 2022 Jun 15;17(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13027-022-00445-z. Infect Agent Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35705991 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide CpG Island Methylation Profiles of Cutaneous Skin with and without HPV Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 28;20(19):4822. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194822. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31569353 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances on the Molecular Mechanism of Cervical Carcinogenesis Based on Systems Biology Technologies.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Feb 7;17:241-250. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.02.001. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 30847042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of exosomal microRNAs in lung cancer biology and clinical applications.Cell Prolif. 2020 Jun;53(6):e12828. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12828. Epub 2020 May 11. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32391938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boulenouar S., Weyn C., Van Noppen M., Moussa Ali M., Favre M., Delvenne P.O., Bex F., Noel A., Englert Y., Fontaine V. Effects of HPV-16 E5, E6 and E7 proteins on survival, adhesion, migration and invasion of trophoblastic cells. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:473–480. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp281. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources