Demethoxycurcumin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticle Downregulates DNA Repair Pathway to Improve Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 30563166
- PMCID: PMC6320861
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23123217
Demethoxycurcumin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticle Downregulates DNA Repair Pathway to Improve Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
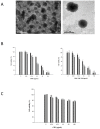
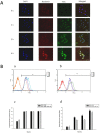
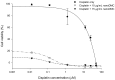
Demethoxycurcumin (DMC), through a self-assembled amphiphilic carbomethyl-hexanoyl chitosan (CHC) nanomatrix has been successfully developed and used as a therapeutic approach to inhibit cisplatin-induced drug resistance by suppressing excision repair cross-complementary 1 (ERCC1) in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells (NSCLC). Previously, DMC significantly inhibited on-target cisplatin resistance protein, ERCC1, via PI3K-Akt-snail pathways in NSCLC. However, low water solubility and bioavailability of DMC causes systemic elimination and prevents its clinical application. To increase its bioavailability and targeting capacity toward cancer cells, a DMC-polyvinylpyrrolidone core phase was prepared, followed by encapsulating in a CHC shell to form a DMC-loaded core-shell hydrogel nanoparticles (DMC-CHC NPs). We aimed to understand whether DMC-CHC NPs efficiently potentiate cisplatin-induced apoptosis through downregulation of ERCC1 in NSCLC. DMC-CHC NPs displayed good cellular uptake efficiency. Dissolved in water, DMC-CHC NPs showed comparable cytotoxic potency with free DMC (dissolved in DMSO). A sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay indicated that DMC-CHC NPs significantly increased cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity by highly efficient intracellular delivery of the encapsulated DMC. A combination of DMC-CHC NPs and cisplatin significantly inhibited on-target cisplatin resistance protein, ERCC1, via the PI3K-Akt pathway. Also, this combination treatment markedly increased the post-target cisplatin resistance pathway including bax, and cytochrome c expressions. Thymidine phosphorylase (TP), a main role of the pyrimidine salvage pathway, was also highly inhibited by the combination treatment. The results suggested that enhancement of the cytotoxicity to cisplatin via administration of DMC-CHC NPs was mediated by down-regulation of the expression of TP, and ERCC1, regulated via the PI3K-Akt pathway.
Keywords: ERCC1; NSCLC; chitosan; demethoxycurcumin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

