Atypical pathogens in hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a worldwide perspective
- PMID: 30563504
- PMCID: PMC6299604
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-018-3565-z
Atypical pathogens in hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a worldwide perspective
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Atypical pathogens in hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a worldwide perspective.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 13;20(1):748. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05472-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33050889 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Empirical antibiotic coverage for atypical pathogens in community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) has long been debated, mainly because of a lack of epidemiological data. We aimed to assess both testing for atypical pathogens and their prevalence in hospitalized patients with CAP worldwide, especially in relation with disease severity.
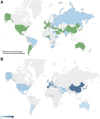
Methods: A secondary analysis of the GLIMP database, an international, multicentre, point-prevalence study of adult patients admitted for CAP in 222 hospitals across 6 continents in 2015, was performed. The study evaluated frequency of testing for atypical pathogens, including L. pneumophila, M. pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae, and their prevalence. Risk factors for testing and prevalence for atypical pathogens were assessed through univariate analysis.
Results: Among 3702 CAP patients 1250 (33.8%) underwent at least one test for atypical pathogens. Testing varies greatly among countries and its frequency was higher in Europe than elsewhere (46.0% vs. 12.7%, respectively, p < 0.0001). Detection of L. pneumophila urinary antigen was the most common test performed worldwide (32.0%). Patients with severe CAP were less likely to be tested for both atypical pathogens considered together (30.5% vs. 35.0%, p = 0.009) and specifically for legionellosis (28.3% vs. 33.5%, p = 0.003) than the rest of the population. Similarly, L. pneumophila testing was lower in ICU patients. At least one atypical pathogen was isolated in 62 patients (4.7%), including M. pneumoniae (26/251 patients, 10.3%), L. pneumophila (30/1186 patients, 2.5%), and C. pneumoniae (8/228 patients, 3.5%). Patients with CAP due to atypical pathogens were significantly younger, showed less cardiovascular, renal, and metabolic comorbidities in comparison to adult patients hospitalized due to non-atypical pathogen CAP.
Conclusions: Testing for atypical pathogens in patients admitted for CAP in poorly standardized in real life and does not mirror atypical prevalence in different settings. Further evidence on the impact of atypical pathogens, expecially in the low-income countries, is needed to guidelines implementation.
Keywords: Atypical pathogens; CAP; Epidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests for this study.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America; American Thoracic Society. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(suppl 2):S27–S72. doi: 10.1086/511159. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramirez JA, Wiemken TL, Peyrani P, Arnold FW, Kelley R, Mattingly WA, Nakamatsu R, Pena S, Guinn BE, Furmanek SP, Persaud AK, Raghuram A, Fernandez F, Beavin L, Bosson R, Fernandez-Botran R, Cavallazzi R, Bordon J, Valdivieso C, Schulte J, Carrico RM. University of Louisville Pneumonia Study Group. Adults hospitalized with pneumonia in the United States: incidence, epidemiology, and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11):1806–1812. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix647. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eliakim-Raz N, Robenshtok E, Shefet D, Gafter-Gvili A, Vidal L, Paul M, Leibovici L. Empiric antibiotic coverage of atypical pathogens for community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 9. Art. No.: CD004418. - PubMed
-
- Arnold FW, Summersgill JT, Ramirez JA. Role of atypical pathogens in the etiology of community-acquired pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2016 Dec;37(6):819–28 Epub 2016 Dec 13. - PubMed
-
- Tao LL, Hu BJ, He LX, Wei L, Xie HM, Wang BQ, Li HY, Chen XH, Zhou CM, Deng WW. Etiology and antimicrobial resistance of community-acquired pneumonia in adult patients in China. Chin Med J. 2012;125(17):2967–2972. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

