Everolimus, a mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, ameliorated streptozotocin-induced learning and memory deficits via neurochemical alterations in male rats
- PMID: 30564080
- PMCID: PMC6295637
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2018-1626
Everolimus, a mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, ameliorated streptozotocin-induced learning and memory deficits via neurochemical alterations in male rats
Abstract
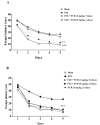
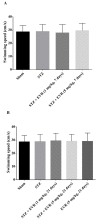
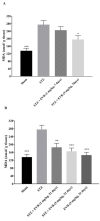
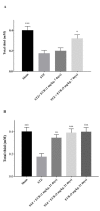
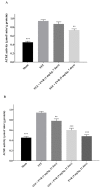
Everolimus (EVR), as a rapamycin analog, is a selective inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase and its associated signaling pathway. mTOR is a serine/threonine protein kinase and its hyperactivity is involved in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and associated cognitive deficits. The present study evaluated the impact of EVR, on cognitive functions, hippocampal cell loss, and neurochemical parameters in the intracerebroventricular streptozotocin (icv-STZ) model of AD rats. EVR (1 and 5 mg/kg) was administered for 21 days following the single administration of STZ (3 mg/kg, icv) or for 7 days on days 21-28 post-STZ injection after establishment of cognitive dysfunction. Cognitive deficits (passive avoidance and spatial memory), oxidative stress parameters, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, and percentage of cell loss were evaluated in the hippocampus. Chronic administration (1 and 5 mg/kg for 21 days from the day of surgery and icv-STZ infusion) or acute injection (5 mg/kg for 7 days after establishment of cognitive impairment) of EVR significantly attenuated cognitive dysfunction, neuronal loss, oxidative stress and AChE activity in the hippocampus of STZ-AD rats. In conclusion, our study showed that EVR could prevent or improve deteriorations in behavioral, biochemical and histopathological features of the icv-STZ rat model of AD. Therefore, inhibition of the hyperactivated mTOR may be an important therapeutic target for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease (AD); acetylcholinesterase; everolimus; mTOR; oxidative stress; streptozotocin.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effect of NAD-299 and TCB-2 on learning and memory, hippocampal BDNF levels and amyloid plaques in Streptozotocin-induced memory deficits in male rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Oct;235(10):2809-2822. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4973-x. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30027497
-
Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Ameliorates Streptozotocin-induced Cognitive and Synaptic Plasticity Deficits by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Preserving AKT and ERK Activities.Curr Med Sci. 2020 Jun;40(3):434-443. doi: 10.1007/s11596-020-2197-x. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Curr Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32681248
-
Effect of curcumin nanoparticles on streptozotocin-induced male Wistar rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Feb;37(2):343-357. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00897-z. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35048324
-
Voglibose attenuates cognitive impairment, Aβ aggregation, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation in streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease rat model.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Oct;31(5):2751-2771. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01313-x. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37665449
-
Cucurbitacin B exerts neuroprotection in a murine Alzheimer's disease model by modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and neurotransmitter levels.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Feb 17;27(2):71. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2702071. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 35227014
Cited by
-
Experimental and clinical tests of FDA-approved kinase inhibitors for the treatment of neurological disorders (update 2024).Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008116. doi: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008116. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Explor Drug Sci. 2025. PMID: 40708570 Free PMC article.
-
Still Living Better through Chemistry: An Update on Caloric Restriction and Caloric Restriction Mimetics as Tools to Promote Health and Lifespan.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 3;21(23):9220. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239220. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33287232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial effects of levetiracetam in streptozotocin-induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Mar;37(3):689-700. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00888-0. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35098412
-
Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidant Therapeutics for Traumatic Brain Injury.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 29;13(3):303. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030303. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of aging and oxidative stress in metabolic and nervous system disorders: programmed cell death and molecular signal transduction crosstalk.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 8;14:1273570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273570. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C. A study of brain insulin receptors, AChE activity and oxidative stress in rat model of ICV STZ induced dementia. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:779–787. - PubMed
-
- Anand P, Singh B. A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res. 2013;36:375–399. - PubMed
-
- Ashrafpour M, Parsaei S, Sepehri H. Quercetin improved spatial memory dysfunctions in rat model of intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced sporadic Alzheimer’sdisease. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol. 2015;5:411–415.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
