A case of prolonged generalized exanthematous pustulosis caused by hydroxychloroquine-Literature review
- PMID: 30564334
- PMCID: PMC6293130
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.1811
A case of prolonged generalized exanthematous pustulosis caused by hydroxychloroquine-Literature review
Abstract
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a self-limited drug reaction. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is an uncommon cause of AGEP with a prolonged recovery course; Thus, the physicians should take the possibility of this rare but severe event in their minds and try to diagnose correctly and better management.
Keywords: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; hydroxychloroquine.
Figures
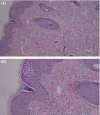

References
-
- Roujeau JC, Bioulac‐Sage P, Bourseau C, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1333‐1338. - PubMed
-
- Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) – a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:113‐119. - PubMed
-
- Halevy S, Kardaun SH, Davidovici B, Wechsler J, EuroSCAR and RegiSCAR Study Group . The spectrum of histopathological features in acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a study of 102 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163(6):1245‐1252. - PubMed
-
- Lotem M, Ingber A, Segal R, Sandbank M. Generalized pustular drug rash induced by hydroxychloroquine. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70:250‐251. - PubMed
-
- Martins A, Lopes LC, Paiva Lopes MJ, Rodrigues JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by hydroxychloroquine. Eur Dermatol. 2006;16:317‐318. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

