ROTf-induced annulation of heteroatom reagents and unsaturated substrates leading to cyclic compounds
- PMID: 30564422
- PMCID: PMC6281944
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.181389
ROTf-induced annulation of heteroatom reagents and unsaturated substrates leading to cyclic compounds
Abstract
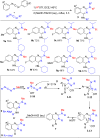
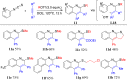
The development of metal-free organic reactions is one of the hotspots in the synthesis of cyclic compounds. ROTf (alkyl trifluoromethanesulfonates), due to their good electrophilicity, are powerful alkylating reagents at heteroatoms such as nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur and phosphorus to induce an electrophilic centre for carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bond formation. Inspired by this chemistry, a variety of research concentrating on heterocycles synthesis has been carried out. In this review, we mainly summarize the ROTf-induced annulation of heteroatom reagents such as nitriles, carbodiimides, azobenzenes, isothiocyanates, aldehydes, isocyanates and phosphaalkene with themselves or alkynes to afford cyclic compounds.
Keywords: annulation; cyclic compounds; heteroatom reagents; trifluoromethanesulfonates.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- Lie JJ, Gribble GW. 2000. Palladium in heterocyclic chemistry. New York, NY: Pergamon Press.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

