The Italian Network for Tumor Bio-Immunotherapy (NIBIT) Foundation: ongoing and prospective activities in immuno-oncology
- PMID: 30564888
- PMCID: PMC11028314
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-018-2286-x
The Italian Network for Tumor Bio-Immunotherapy (NIBIT) Foundation: ongoing and prospective activities in immuno-oncology
Abstract
The ongoing revolution in cancer immunotherapy stems from the knowledge that distinct immune-checkpoints regulate the physiological crosstalk between and among immune cells by delivering inhibitory or activating signals. These notions, and the availability of mAb directed to diverse immune-checkpoint molecules, have led to a significant clinical improvement in cancer treatment. In this scenario, further achievements are undoubtedly to be expected from the contribution of novel, proof-of-principle clinical trials designed to explore the therapeutic efficacy of new immunotherapy-based combinations and treatment sequences. Along these lines, the clinical translation of pre-clinical evidence generated by non-profit research entities is likely to provide a significant contribution to gaining new insights that will further boost the field of cancer immunotherapy. To pursue this goal, and to provide comprehensive educational programs in immune-oncology (I-O), several national and global networks have been revitalized or newly established in recent years. This rapidly evolving scenario led the Board of Directors of the Italian Network of Tumor Bio-Immunotherapy (NIBIT) to establish the NIBIT Foundation. This Focused Research Review summarizes the main ongoing and prospective I-O activities of the NIBIT Foundation.
Keywords: Clinical trials; Immune-oncology; Immunotherapy; Melanoma; Mesothelioma; NIBIT.
Conflict of interest statement
Anna Maria Di Giacomo served on the advisory board of Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Pierre Fabre, Glaxo Smith Kline and she is a member of the scientific board of directors of the NIBIT Foundation; Ramy Ibrahim is a member of the scientific advisory board of: Arcus, Harpoon, Immunovaccine and ImaginAB;Jaclyn Lyman is a PICI employee; Pier Giorgio Natali is a member of the scientific board of directors of the NIBIT Foundation; Michele Maio served on advisory boards of Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche-Genentech, Merck Sharp Dohme and AstraZeneca-MedImmune, and he is the president of the NIBIT Foundation. The authors declare that there are no other conflicts of interest.
Figures
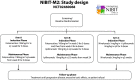
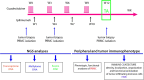
References
-
- Maio M, Fonsatti E. The Italian Network for Tumor Biotherapy (NIBIT): past, present and future goals. Rev Health Care. 2014;5(1):3–6. doi: 10.7175/rhc.v5i1.896. - DOI
-
- Maio M, Lofiego MF, Fazio C, Cannito S, Chiarucci C, Giacobini G, Valente M, Tunici P, Covre A, Russo V. Fifteenth Meeting of the Network Italiano per la Bioterapia dei Tumori (NIBIT) on Cancer Bio-Immunotherapy, Siena, Italy, October 5–7, 2017. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018 doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2222-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Korn EL, Liu PY, Lee SJ, Chapman JA, Niedzwiecki D, Suman VJ, Moon J, Sondak VK, Atkins MB, Eisenhauer EA, Parulekar W, Markovic SN, Saxman S, Kirkwood JM. Meta-analysis of phase II cooperative group trials in metastatic stage IV melanoma to determine progression-free and overall survival benchmarks for future phase II trials. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(4):527–534. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.12.7837. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Margolin K, Ernstoff MS, Hamid O, Lawrence D, McDermott D, Puzanov I, Wolchok JD, Clark JI, Sznol M, Logan TF, Richards J, Michener T, Balogh A, Heller KN, Hodi FS. Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases: an open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:459–465. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70090-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Di Giacomo AM, Ascierto PA, Pilla L, Santinami M, Ferrucci PF, Giannarelli D, Marasco A, Rivoltini L, Simeone E, Nicoletti SV, Fonsatti E, Annesi D, Queirolo P, Testori A, Ridolfi R, Parmiani G, Maio M. Ipilimumab and fotemustine in patients with advanced melanoma (NIBIT-M1): an open-label, single-arm phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:879–886. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70324-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

