Kalirin-7 prevents dendritic spine dysgenesis induced by amyloid beta-derived oligomers
- PMID: 30565792
- PMCID: PMC6559832
- DOI: 10.1111/ejn.14311
Kalirin-7 prevents dendritic spine dysgenesis induced by amyloid beta-derived oligomers
Abstract
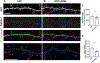
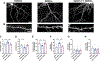
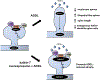
Synapse degeneration and dendritic spine dysgenesis are believed to be crucial early steps in Alzheimer's disease (AD), and correlate with cognitive deficits in AD patients. Soluble amyloid beta (Aβ)-derived oligomers, also termed Aβ-derived diffusible ligands (ADDLs), accumulate in the brain of AD patients and play a crucial role in AD pathogenesis. ADDLs bind to mature hippocampal neurons, induce structural changes in dendritic spines and contribute to neuronal death. However, mechanisms underlying structural and toxic effects are not fully understood. Here, we report that ADDLs bind to cultured mature cortical pyramidal neurons and induce spine dysgenesis. ADDL treatment induced the rapid depletion of kalirin-7, a brain-specific guanine-nucleotide exchange factor for the small GTPase Rac1, from spines. Kalirin-7 is a key regulator of dendritic spine morphogenesis and maintenance in forebrain pyramidal neurons and here we show that overexpression of kalirin-7 prevents ADDL-induced spine degeneration. Taken together, our results suggest that kalirin-7 may play a role in the early events leading to synapse degeneration, and its pharmacological activation may prevent or delay synapse pathology in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Rac1; guanine-nucleotide exchange factors; synapse.
© 2018 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have completing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures

References
-
- Almeida CG, Tampellini D, Takahashi RH, Greengard P, Lin MT, Snyder EM and Gouras GK (2005) Beta-amyloid accumulation in APP mutant neurons reduces PSD-95 and GluR1 in synapses. Neurobiol Dis, 20, 187–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

