Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in combination with S-1/capecitabine plus oxaliplatin in patients with previously untreated, unresectable, advanced, or recurrent gastric/gastroesophageal junction cancer: interim results of a randomized, phase II trial (ATTRACTION-4)
- PMID: 30566590
- PMCID: PMC6386029
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdy540
Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in combination with S-1/capecitabine plus oxaliplatin in patients with previously untreated, unresectable, advanced, or recurrent gastric/gastroesophageal junction cancer: interim results of a randomized, phase II trial (ATTRACTION-4)
Abstract
Background: Nivolumab is approved as an option for third- or later-line treatment of advanced gastric/gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) cancer in several countries after ATTRACTION-2. To further improve the therapeutic efficacy of first-line therapy, exploration of a nivolumab-chemotherapy combination is warranted. In part 1 (phase II) of ATTRACTION-4, the safety and efficacy of nivolumab combined with S-1 plus oxaliplatin (SOX) or capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (CapeOX) as first-line therapy for unresectable advanced or recurrent human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative G/GEJ cancer were evaluated.
Patients and methods: Patients were randomized (1 : 1) to receive nivolumab (360 mg intravenously every 3 weeks) plus SOX (S-1, 40 mg/m2 orally twice daily for 14 days followed by 7 days off; oxaliplatin, 130 mg/m2 intravenously on day 1 every 3 weeks) or CapeOX (capecitabine, 1000 mg/m2 orally twice daily for 14 days followed by 7 days off; oxaliplatin, 130 mg/m2 intravenously on day 1 every 3 weeks) until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or consent withdrawal.
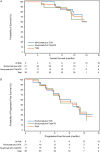
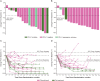
Results: Of 40 randomized patients, 39 (nivolumab plus SOX, 21; nivolumab plus CapeOX, 18) and 38 (21 and 17, respectively) comprised the safety and efficacy populations, respectively. Most frequent (>10%) grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events were neutropenia (14.3%) in the nivolumab plus SOX group, and neutropenia (16.7%), anemia, peripheral sensory neuropathy, decreased appetite, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and nausea (11.1% each) in the nivolumab plus CapeOX group. No treatment-related death occurred. Objective response rate was 57.1% (95% confidence interval 34.0-78.2) with nivolumab plus SOX and 76.5% (50.1-93.2) with nivolumab plus CapeOX. Median overall survival was not reached (NR) in both groups. Median progression-free survival was 9.7 months (5.8-NR) and 10.6 months (5.6-12.5), respectively.
Conclusion: Nivolumab combined with SOX/CapeOX was well tolerated and demonstrated encouraging efficacy for unresectable advanced or recurrent HER2-negative G/GEJ cancer. ATTRACTION-4 has proceeded to part 2 (phase III) to compare nivolumab plus SOX/CapeOX versus placebo plus SOX/CapeOX.
Clinicaltrials.gov id: NCT02746796.
Keywords: S-1; capecitabine; gastric/gastroesophageal cancer; nivolumab; oxaliplatin; programmed death-1.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M. et al. GLOBOCAN 2012: estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012 v1.0. IARC CancerBase No. 11. International Agency for Research on Cancer; http://globocan.iarc.fr (16 November 2018, date last accessed).
-
- Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Almhanna K. et al. Gastric cancer, version 3.2016, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2016; 14(10): 1286–1312. - PubMed
-
- Smyth EC, Verheij M, Allum W. et al. Gastric cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2016; 27(Suppl 5): v38–v49. - PubMed
-
- Okines AF, Norman AR, McCloud P. et al. Meta-analysis of the REAL-2 and ML17032 trials: evaluating capecitabine-based combination chemotherapy and infused 5-fluorouracil-based combination chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced oesophago-gastric cancer. Ann Oncol 2009; 20(9): 1529–1534. - PubMed
-
- Yamada Y, Higuchi K, Nishikawa K. et al. Phase III study comparing oxaliplatin plus S-1 with cisplatin plus S-1 in chemotherapy-naïve patients with advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol 2015; 26(1): 141–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

