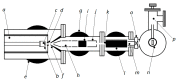
Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles Using a Gas Phase Nanocluster Device and Preliminary Biological Uses
- PMID: 30567288
- PMCID: PMC6316590
- DOI: 10.3390/ma11122574
Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles Using a Gas Phase Nanocluster Device and Preliminary Biological Uses
Abstract
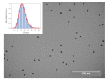
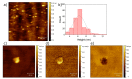
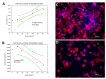
Nanoparticles can be used in a large variety of applications, including magnetic sensing, biological, superconductivity, tissue engineering, and other fields. In this study, we explore the fabrication of gas phase silver nanoparticles using a sputtering evaporation source. This setup composed of a dual magnetron cluster source holds several advantages over other techniques. The system has independent control over the cluster concentration and a wide range of cluster size and materials that can be used for the clusters and for the matrix where it can be embedded. Characterization of these silver nanoparticles was done using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). We obtain a lateral width of 10.6 nm with a dispersion of 0.24 nm. With atomic force microscopy (AFM) a Gaussian fit of this distribution yields and average height of 6.3 nm with a standard deviation of 1.4 nm. We confirm that the deposited silver nanoparticles have a homogenous area distribution, that they have a defined shape and size distribution, and that they are single standing nanoparticles. Given that the scientific literature is not precise regarding the toxic concentration of the nanoparticles, devices such as ours can help clarify these questions. In order to explore further biological applications, we have done preliminary experiments of cell spreading (myoblast adhesion), obtaining interesting morphological changes correlated with the silver concentration on the surface. With a deposited silver concentration ranging from 100⁻620 ng/cm², the cells showed morphological changes in a short time of 2 h. We conclude that this high precision nanoparticle fabrication technique is adequate for further biological research.
Keywords: gas phase clusters; metallic clusters; myoblast cells; nanoparticles; silver clusters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Canali L. Novel Scanning Probes Applied to the Study of Nanostructures. Delft University of Technology; Delft, The Netherlands: 2000.
-
- Reinhard P.G., Suraud E. Introduction to Cluster Dynamics. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH; Weinheim, Germany: 2004. p. 40.
-
-
Suzhou SinoRaybo Nanotechnology Co., Ltd., Zone D, No. 99, Ren’ai Road, Suzhou Industrial Park.
-
-
- Morris J.E. Nanopackaging: Nanotechnologies and Electronics Packaging. In: Morris J., editor. Nanopackaging. Springer; Boston, MA, USA: 2008.
-
- Solairajan S.A., Alexraj S., Kumar G.P., Rajan V.P. Review on nano fabrication and application. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014;984–985:508–513. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.984-985.508. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

