A Resazurin Reduction-Based Assay for Rapid Detection of Polymyxin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 30567745
- PMCID: PMC6425163
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01563-18
A Resazurin Reduction-Based Assay for Rapid Detection of Polymyxin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
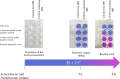
A rapid test was developed for identification of polymyxin resistance in nonfermenting bacteria. This test detects viable cells after growth in a medium containing a defined concentration of colistin. The principle of this test is based on the visual detection of the reduction of the resazurin reagent, a viability colorant, as observed by its color change (blue to purple or pink). Its evaluation was performed by using 92 colistin-resistant and colistin-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Sensitivity and specificity were found to be 100% and 95%, respectively, by comparison with the standard broth microdilution method. The Rapid ResaPolymyxin Acinetobacter/Pseudomonas NP test is inexpensive, easy to perform, highly sensitive and specific, and can be completed in 4 hours. It could be useful in countries facing endemic spread of colistin-resistant nonfermenters.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; colistin; rapid diagnostic test; susceptibility testing.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Vincent J-L, Rello J, Marshall J, Silva E, Anzueto A, Martin CD, Moreno R, Lipman J, Gomersall C, Sakr Y, Reinhart K, EPIC II Group of Investigators. 2009. International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA 302:2323–2329. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1754. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

