Autophagy-dependent cell death
- PMID: 30568239
- PMCID: PMC6460387
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-018-0252-y
Autophagy-dependent cell death
Abstract
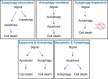
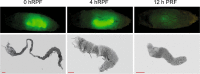
Autophagy-dependent cell death can be defined as cell demise that has a strict requirement of autophagy. Although autophagy often accompanies cell death following many toxic insults, the requirement of autophagic machinery for cell death execution, as established through specific genetic or chemical inhibition of the process, is highly contextual. During animal development, perhaps the best validated model of autophagy-dependent cell death is the degradation of the larval midgut during larval-pupal metamorphosis, where a number of key autophagy genes are required for the removal of the tissues. Surprisingly though, even in the midgut, not all of the 'canonical' autophagic machinery appears to be required. In other organisms and cancer cells many variations of autophagy-dependent cell death are apparent, pointing to the lack of a unifying cell death pathway. It is thus possible that components of the autophagy machinery are selectively utilised or repurposed for this type of cell death. In this review, we discuss examples of cell death that utilise autophagy machinery (or part thereof), the current knowledge of the complexity of autophagy-dependent cellular demise and the potential mechanisms and regulatory pathways involved in such cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ellis RE, Yuan JY, Horvitz HR. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–98. - PubMed
-
- Cashio P, Lee TV, Bergmann A. Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila melanogaster. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005;16:225–35. - PubMed
-
- White K, Grether ME, Abrams JM, Young L, Farrell K, Steller H. Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila. Science. 1994;264:677–83. - PubMed
-
- Ellis HM, Horvitz HR. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1986;44:817–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

