Physical Function, Frailty, Cognition, Depression, and Quality of Life in Hospitalized Adults ≥60 Years With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure With Preserved Versus Reduced Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 30571197
- PMCID: PMC6380360
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.118.005254
Physical Function, Frailty, Cognition, Depression, and Quality of Life in Hospitalized Adults ≥60 Years With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure With Preserved Versus Reduced Ejection Fraction
Abstract
Background: Older hospitalized acute decompensated heart failure (HF) patients have persistently poor outcomes and delayed recovery regardless of ejection fraction (EF). We hypothesized that impairments in physical function, frailty, cognition, mood, and quality of life (QoL) potentially contributing to poor clinical outcomes would be similarly severe in acute decompensated HF patients ≥60 years of age with preserved versus reduced EF (HFpEF and HFrEF).
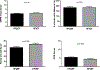
Methods and results: In 202 consecutive older (≥60 years) hospitalized acute decompensated HF patients in a multicenter trial, we prospectively performed at baseline: short physical performance battery, 6-minute walk distance, frailty assessment, Geriatric Depression Scale, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, and QoL assessments. Older acute decompensated HFpEF (EF ≥45%, n=96) and HFrEF (EF <45%, n=106) patients had similar impairments in all physical function measures (short physical performance battery [5.9±0.3 versus 6.2±0.2]; 6-minute walk distance [184±10 versus 186±9 m]; and gait speed [0.60±0.02 versus 0.61±0.02 m/s]) and rates of frailty (55% versus 52%; P=0.70) and cognitive impairment (77% versus 81%; P=0.56) when adjusted for differences in sex, body mass index, and comorbidities. However, depression and QoL were consistently worse in HFpEF versus HFrEF. Depression was usually unrecognized clinically with 38% having Geriatric Depression Scale ≥5 and no documented history of depression.
Conclusions: Patients ≥60 years hospitalized with acute decompensated HF patients have broad, marked impairments in physical function and high rates of frailty and impaired cognition: these impairments are similar in HFpEF versus HFrEF. Further, depression was common and QoL was reduced, and both were worse in HFpEF than HFrEF. Depression was usually unrecognized clinically. These findings suggest opportunities for novel interventions to improve these important patient-centered outcomes.
Clinical trial registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov . Unique identifier: NCT02196038.
Keywords: aging; depression; frailty; heart failure; quality of life.
Figures
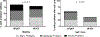

Comment in
-
Lessons From the First 202 REHAB-HF Participants.Circ Heart Fail. 2018 Nov;11(11):e005611. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.118.005611. Circ Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 30571199 No abstract available.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Mackey RH, Matsushita K, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Thiagarajan RR, Reeves MJ, Ritchey M, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sasson C, Towfighi A, Tsao CW, Turner MB, Virani SS, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P, American Heart Association Statistics C and Stroke Statistics S. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e146–e603. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shah KS, Xu H, Matsouaka RA, Bhatt DL, Heidenreich PA, Hernandez AF, Devore AD, Yancy CW and Fonarow GC. Heart Failure With Preserved, Borderline, and Reduced Ejection Fraction: 5-Year Outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:2476–2486. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Albert NM, Allen LA, Bluemke DA, Butler J, Fonarow GC, Ikonomidis JS, Khavjou O, Konstam MA, Maddox TM, Nichol G, Pham M, Pina IL and Trogdon JG. Forecasting the impact of heart failure in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6:606–19. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

