Lack of Suppression of Aldosterone Production Leads to Salt-Sensitive Hypertension in Female but Not Male Balb/C Mice
- PMID: 30571230
- PMCID: PMC6309424
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11303
Lack of Suppression of Aldosterone Production Leads to Salt-Sensitive Hypertension in Female but Not Male Balb/C Mice
Abstract
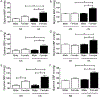
Clinical studies indicate that salt-sensitive hypertension is more prevalent in women than in men. However, animal models of salt sensitivity have primarily focused on the mechanisms of salt sensitivity in male animals; therefore, elucidation of these mechanisms in female animal models is needed. We have previously shown that female Balb/C mice have higher aldosterone synthase expression and aldosterone production than males. We hypothesized that female Balb/C mice develop salt-sensitive increases in blood pressure. Seven-day feeding of a 4% NaCl high-salt (HS) diet increased blood pressure in female mice without altering blood pressure in males. Females on an HS diet displayed no apparent increases in sodium retention as assessed by 24-hour urine collection, sodium balance measure, and saline loading excretion analysis. Females on an HS diet exhibited lower renin-angiotensin system activity (plasma Ang II [angiotensin II], plasma renin activity, and ACE [angiotensin-converting enzyme] activity) compared with males but developed a salt-induced elevation in adrenal aldosterone synthase expression and retained higher aldosterone levels than males on HS. This resulted in a higher aldosterone/plasma renin activity ratio in females compared with males on HS feeding. Adrenal mRNA expression of angiotensinogen and leptin receptor was increased in female mice on an HS diet. HS impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation in female mice only. MR (mineralocorticoid receptor) inhibition (eplerenone) restored blood pressure and endothelial function in females on an HS diet. Collectively, these data indicate that Balb/C mice develop sex-discrepant salt-sensitive hypertension likely via aldosterone-MR-mediated mechanisms involving impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation in females only. This study presents the first model of spontaneous sex-specific salt sensitivity, which mimics the human pathology.
Keywords: adrenal cortex; aldosterone; endothelium; hypertension; mouse, Balb C; renin-angiotensin system; sex characteristics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
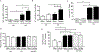
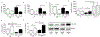
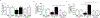

References
-
- Fryar CD, Ostchega Y, Hales CM, Zhang G, Kruszon-Moran D. Hypertension prevalence and control among adults: United states, 2015–2016. NCHS Data Brief 2017:1–8 - PubMed
-
- Huang CL, Kuo E. Mechanisms of disease: Wnk-ing at the mechanism of salt-sensitive hypertension. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2007;3:623–630 - PubMed
-
- Iatrino R, Manunta P, Zagato L. Salt sensitivity: Challenging and controversial phenotype of primary hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 2016;18:70. - PubMed
-
- Van Vliet BN, Montani JP. The time course of salt-induced hypertension, and why it matters. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32 Suppl 6:S35–47 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

