Machine Learning Outperforms ACC / AHA CVD Risk Calculator in MESA
- PMID: 30571498
- PMCID: PMC6404456
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009476
Machine Learning Outperforms ACC / AHA CVD Risk Calculator in MESA
Abstract
Background Studies have demonstrated that the current US guidelines based on American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator may underestimate risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease ( CVD ) in certain high-risk individuals, therefore missing opportunities for intensive therapy and preventing CVD events. Similarly, the guidelines may overestimate risk in low risk populations resulting in unnecessary statin therapy. We used Machine Learning ( ML ) to tackle this problem. Methods and Results We developed a ML Risk Calculator based on Support Vector Machines ( SVM s) using a 13-year follow up data set from MESA (the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) of 6459 participants who were atherosclerotic CVD-free at baseline. We provided identical input to both risk calculators and compared their performance. We then used the FLEMENGHO study (the Flemish Study of Environment, Genes and Health Outcomes) to validate the model in an external cohort. ACC / AHA Risk Calculator, based on 7.5% 10-year risk threshold, recommended statin to 46.0%. Despite this high proportion, 23.8% of the 480 "Hard CVD " events occurred in those not recommended statin, resulting in sensitivity 0.76, specificity 0.56, and AUC 0.71. In contrast, ML Risk Calculator recommended only 11.4% to take statin, and only 14.4% of "Hard CVD " events occurred in those not recommended statin, resulting in sensitivity 0.86, specificity 0.95, and AUC 0.92. Similar results were found for prediction of "All CVD " events. Conclusions The ML Risk Calculator outperformed the ACC/AHA Risk Calculator by recommending less drug therapy, yet missing fewer events. Additional studies are underway to validate the ML model in other cohorts and to explore its ability in short-term CVD risk prediction.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Machine learning; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease prevention; cardiovascular disease risk factors; cardiovascular risk; clinical decision support; prediction statistics; statin.
Figures

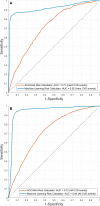
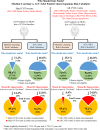
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Mackey RH, Matsushita K, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Thiagarajan RR, Reeves MJ, Ritchey M, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sasson C, Towfighi A, Tsao CW, Turner MB, Virani SS, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P; American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee . Heart disease and stroke statistics‐2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e146–e603. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goff DC, Lloyd‐Jones DM, Bennett G, Coady S, D'Agostino RB, Gibbons R, Greenland P, Lackland DT, Levy D, O'Donnell CJ, Robinson JG, Schwartz JS, Shero ST, Smith SC, Sorlie P, Stone NJ, Wilson PW, Jordan HS, Nevo L, Wnek J, Anderson JL, Halperin JL, Albert NM, Bozkurt B, Brindis RG, Curtis LH, DeMets D, Hochman JS, Kovacs RJ, Ohman EM, Pressler SJ, Sellke FW, Shen WK, Tomaselli GF; American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines . 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the assessment of cardiovascular risk: a report of the American College Of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129:S49–S73. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Cook NR. Statins: new American guidelines for prevention of cardiovascular disease. Lancet. 2013;382:1762–1765. - PubMed
-
- Kavousi M, Leening MJ, Nanchen D, Greenland P, Graham IM, Steyerberg EW, Ikram MA, Stricker BH, Hofman A, Franco OH. Comparison of application of the ACC/AHA guidelines, Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines, and European Society of Cardiology guidelines for cardiovascular disease prevention in a European Cohort. JAMA. 2014;311:1416–1423. - PubMed

