IL-6 stimulation of DNA replication is JAK1/2 mediated in cross-talk with hyperactivated ERK1/2 signaling
- PMID: 30571852
- PMCID: PMC6347554
- DOI: 10.1002/cbin.11084
IL-6 stimulation of DNA replication is JAK1/2 mediated in cross-talk with hyperactivated ERK1/2 signaling
Abstract
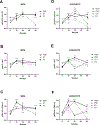
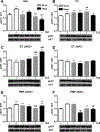
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are developing resistance to therapy by JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib. To explore the mechanism of ruxolitinib's limited effect, we examined the JAK1/2 mediated induction of proliferation related ERK1/2 and AKT signaling by proinflammatory interleukin-6 (IL-6) in MPN granulocytes and JAK2V617F mutated human erythroleukemia (HEL) cells. We found that JAK1/2 or JAK2 inhibition prevented the IL-6 activation of STAT3 and AKT pathways in polycythemia vera and HEL cells. Further, we showed that these inhibitors also blocked the IL-6 activation of the AKT pathway in primary myelofibrosis (PMF). Only JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib largely activated ERK1/2 signaling in essential thrombocythemia and PMF (up to 4.6 fold), with a more prominent activation in JAK2V617F positive granulocytes. Regarding a cell cycle, we found that IL-6 reduction of HEL cells percentage in G2M phase was reversed by ruxolitinib (2.6 fold). Moreover, ruxolitinib potentiated apoptosis of PMF granulocytes (1.6 fold). Regarding DNA replication, we found that ruxolitinib prevented the IL-6 augmentation of MPN granulocytes frequency in the S phase of the cell cycle (up to 2.9 fold). The inflammatory stimulation induces a cross-talk between the proliferation linked pathways, where JAK1/2 inhibition is compensated by the activation of the ERK1/2 pathway during IL-6 stimulation of DNA replication.
Keywords: ERK1/2 signaling; JAK1/2 inhibition; cell cycle; inflammation; myeloproliferative neoplasm.
© 2018 International Federation for Cell Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Efficacy of JAK1/2 inhibition in murine myeloproliferative neoplasms is not mediated by targeting oncogenic signaling.Nat Commun. 2025 May 24;16(1):4833. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60019-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40413183 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical characterization of the selective JAK1/2 inhibitor INCB018424: therapeutic implications for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms.Blood. 2010 Apr 15;115(15):3109-17. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-214957. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20130243 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of JAK1/2 inhibition on bone marrow stromal cells of myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) patients and healthy individuals.Eur J Haematol. 2018 Jul;101(1):57-67. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13079. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Eur J Haematol. 2018. PMID: 29645296
-
The Development and Use of Janus Kinase 2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2017 Aug;31(4):613-626. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 May 17. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28673391 Review.
-
Myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders: State of the art.Hematol Oncol. 2020 Apr;38(2):121-128. doi: 10.1002/hon.2701. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31833567 Review.
Cited by
-
An updated review of the pharmacological effects and potential mechanisms of hederagenin and its derivatives.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1374264. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1374264. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38962311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VEGF Regulation of Angiogenic Factors via Inflammatory Signaling in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 22;22(13):6671. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136671. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206393 Free PMC article.
-
Multilevel defects in the hematopoietic niche in essential thrombocythemia.Haematologica. 2020 Mar;105(3):661-673. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.213686. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 31289202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araki M, Yang Y, Masubuchi N, Hironaka Y, Takei H, Morishita S, et al. (2016). Activation of the thrombopoietin receptor by mutant calreticulin in CALR-mutant myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood, 127(10), 1307–1316. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee M, Stühmer T, Herrmann P, Bommert K, Dörken B, Bargou RC (2004). Combined disruption of both the MEK/ERK and the IL-6R/STAT3 pathways is required to induce apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells in the presence of bone marrow stromal cells. Blood, 104(12), 3712–3721. - PubMed
-
- Chen YY, Huang CE, Lee KD, Chen CC (2016). Clinical efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib in the management of myelofibrosis: A single institution experience in Taiwan. Hematology, 21(1), 3–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Z01 DK025061/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- IZ73Z0 152420/1/Swiss National Science Foundation through Joint research project (SCOPES)
- Intramural Research Program at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH, Bethesda, USA
- OI175053/Serbian Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

