Brain and cognitive correlates of subjective cognitive decline-plus features in a population-based cohort
- PMID: 30572953
- PMCID: PMC6302483
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-018-0449-9
Brain and cognitive correlates of subjective cognitive decline-plus features in a population-based cohort
Abstract
Background: Subjective cognitive decline (SCD) consists of self-perceived decline in cognition over time. The occurrence of specific additional features in SCD (so-called SCDplus) confers a higher risk of future cognitive decline. However, it is not known whether SCDplus patients have a distinct cognitive and neuroimaging profile. Therefore, we aimed to study the associations between SCDplus features and cognitive and neuroimaging profiles in a population-based cohort.
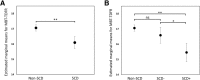
Methods: A total of 2670 individuals from the ALFA cohort underwent clinical, cognitive, and MRI (n = 532) explorations. Subjects were classified as self-reporting cognitive decline (SCD) or not self-reporting cognitive decline (non-SCD). Within the SCD group, participants were also classified according to the number of SCDplus features they met (SCD+, > 3; SCD-, ≤ 3).
Results: The prevalence of SCD in the cohort was 21.4% (55.8% SCD-, 44.2% SCD+). SCD+ subjects performed worse than non-SCD and SCD- subjects in memory and executive function. Among the SCDplus features, confirmation of decline by an informant was the best predictor of worse cognitive performance and lower gray matter volumes.
Conclusions: Our findings show that individuals with SCDplus features have a distinct cognitive and brain volumetric profile similar to that found in Alzheimer's disease and therefore support the use of the SCDplus concept as an enrichment criterion in population-based cohorts.
Keywords: Memory; Subjective cognitive decline; Voxel-based morphometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the local ethics committee and all individuals gave written informed consent to participate.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Cacciamani F, Tandetnik C, Gagliardi G, Bertin H, Habert M-O, Hampel H, et al. Low cognitive awareness, but not complaint, is a good marker of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;59:753–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

