Combination of flow cytometry and functional imaging for monitoring of residual disease in myeloma
- PMID: 30573775
- PMCID: PMC6586541
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-018-0329-0
Combination of flow cytometry and functional imaging for monitoring of residual disease in myeloma
Abstract
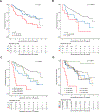
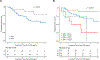
The iliac crest is the sampling site for minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring in multiple myeloma (MM). However, the disease distribution is often heterogeneous, and imaging can be used to complement MRD detection at a single site. We have investigated patients in complete remission (CR) during first-line or salvage therapy for whom MRD flow cytometry and the two imaging modalities positron emission tomography (PET) and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) were performed at the onset of CR. Residual focal lesions (FLs), detectable in 24% of first-line patients, were associated with short progression-free survival (PFS), with DW-MRI detecting disease in more patients. In some patients, FLs were only PET positive, indicating that the two approaches are complementary. Combining MRD and imaging improved prediction of outcome, with double-negative and double-positive features defining groups with excellent and dismal PFS, respectively. FLs were a rare event (12%) in first-line MRD-negative CR patients. In contrast, patients achieving an MRD-negative CR during salvage therapy frequently had FLs (50%). Multi-region sequencing and imaging in an MRD-negative patient showed persistence of spatially separated clones. In conclusion, we show that DW-MRI is a promising tool for monitoring residual disease that complements PET and should be combined with MRD.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
Bart Barlogie is a co-inventor on patents and patent applications related to use of GEP in cancer medicine that have been licensed to Quest diagnostics. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
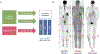

Similar articles
-
Predictive role of diffusion-weighted whole-body MRI (DW-MRI) imaging response according to MY-RADS criteria after autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma and combined evaluation with MRD assessment by flow cytometry.Cancer Med. 2021 Sep;10(17):5859-5865. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4136. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34263564 Free PMC article.
-
[Impact of minimal residual disease detection after treatment of multiple myeloma].Orv Hetil. 2019 Mar;160(13):502-508. doi: 10.1556/650.2019.31353. Orv Hetil. 2019. PMID: 30907098 Hungarian.
-
Minimal residual disease assessed by multiparameter flow cytometry in multiple myeloma: impact on outcome in the Medical Research Council Myeloma IX Study.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jul 10;31(20):2540-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.2119. Epub 2013 Jun 3. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23733781 Clinical Trial.
-
Functional Imaging for Therapeutic Assessment and Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Multiple Myeloma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5406. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155406. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRD Assessment in Multiple Myeloma: Progress and Challenges.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2021 Apr;16(2):162-171. doi: 10.1007/s11899-021-00633-5. Epub 2021 May 5. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2021. PMID: 33950462 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimal Residual Disease in Multiple Myeloma: State of the Art and Future Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2020 Jul 7;9(7):2142. doi: 10.3390/jcm9072142. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32645952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimal residual disease (mrd) in multiple myeloma: prognostic and therapeutic implications (including imaging).Hemasphere. 2019 Jun 30;3(Suppl):124-126. doi: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000243. eCollection 2019 Jun. Hemasphere. 2019. PMID: 35309827 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Utility of Euroflow MRD Assessment in Real-World Multiple Myeloma Practice.Front Oncol. 2022 May 18;12:820605. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.820605. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35664737 Free PMC article.
-
Choline PET/CT in Multiple Myeloma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 28;12(6):1394. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061394. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32481661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual assessment with multiparameter flow cytometry and 18F-FDG PET/CT scan provides enhanced prediction of measurable residual disease after autologous haemopoietic stem cell transplant in myeloma-a prospective study.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023 Sep;58(9):1045-1047. doi: 10.1038/s41409-023-02017-0. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37328681 No abstract available.
References
-
- Avet-Loiseau H, Lauwers-Cances V, Corre J, Moreau P, Attal M, Munshi N. Minimal Residual Disease in Multiple Myeloma: Final Analysis of the IFM2009 Trial, Abstract 435. ASH 59th Annual Meeting & Exposition, December 2017 2017.
-
- Lahuerta JJ, Paiva B, Vidriales MB, Cordon L, Cedena MT, Puig N, et al. Depth of Response in Multiple Myeloma: A Pooled Analysis of Three PETHEMA/GEM Clinical Trials. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2017. September 1; 35(25): 2900–2910. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

