Impact of Dietary Carbohydrate/Protein Ratio on Hepatic Metabolism in Land-Locked Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.)
- PMID: 30574094
- PMCID: PMC6291493
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01751
Impact of Dietary Carbohydrate/Protein Ratio on Hepatic Metabolism in Land-Locked Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.)
Abstract
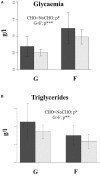
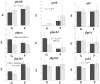
A common-garden experiment was carried out to compare two genetically distinct strains of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fed diets with either high (CHO) or low (NoCHO) digestible carbohydrate (starch). Twenty salmon from either a commercial farmed strain (F) or a land-locked population (G) were placed in two tanks (10 fish of each population in each tank) and fed either CHO or NoCHO feeds. At the end of the experiment fish were fasted for 8 h, euthanized and blood and liver collected. Both diet and population had an effect on circulating glucose levels with G showing hypoglycaemia and dietary starch increasing this parameter. In contrast, G showed increased plasma triacylglycerol levels regardless of dietary treatment suggesting faster conversion of glucose to triacylglycerol. This different ability to metabolize dietary starch among strains was also reflected at a molecular (gene) level as most of the metabolic pathways evaluated were mainly affected by the factor population rather than by diet. The data are promising and suggest different regulatory capacities toward starch utilization between land-locked salmon and the farmed stock. Further analyses are necessary in order to fully characterize the capacity of land-locked salmon to utilize dietary carbohydrate.
Keywords: dietary carbohydrates; glucose metabolism; land-locked; salmon populations; transcriptomics.
Figures


References
-
- Bermejo-Nogales A., Calduch-Giner J. A., Pérez-Sánchez J. (2015). Unraveling the molecular signatures of oxidative phosphorylation to cope with the nutritionally changing metabolic capabilities of liver and muscle tissues in farmed fish. PLoS One 10:e0122889. 10.1371/journal.pone.0122889 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Betancor M. B., Olsen R. E., Solstorm D., Skulstad O. F., Tocher D. R. (2016). Assessment of a land-locked atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) population as a potential genetic resource with a focus on long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1861 227–238. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.12.015 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Betancor M. B., Sprague M., Sayanova O., Usher S., Campbell P. J., Napier J. A., et al. (2015a). Evaluation of a high-EPA oil from transgenic Camelina sativa in feeds for atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): effects on tissue fatty acid composition, histology and gene expression. Aquaculture 444 1–12. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

