The C-Terminal Transactivation Domain of STAT1 Has a Gene-Specific Role in Transactivation and Cofactor Recruitment
- PMID: 30574148
- PMCID: PMC6291510
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02879
The C-Terminal Transactivation Domain of STAT1 Has a Gene-Specific Role in Transactivation and Cofactor Recruitment
Abstract
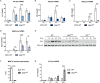
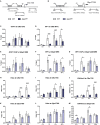
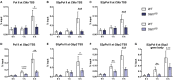
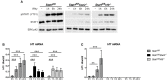
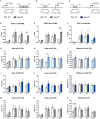
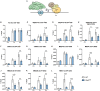
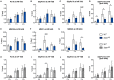
STAT1 has a key role in the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity by inducing transcriptional changes in response to cytokines, such as all types of interferons (IFN). STAT1 exist as two splice isoforms, which differ in regard to the C-terminal transactivation domain (TAD). STAT1β lacks the C-terminal TAD and has been previously reported to be a weaker transcriptional activator than STAT1α, although this was strongly dependent on the target gene. The mechanism of this context-dependent effects remained unclear. By using macrophages from mice that only express STAT1β, we investigated the role of the C-terminal TAD during the distinct steps of transcriptional activation of selected target genes in response to IFNγ. We show that the STAT1 C-terminal TAD is absolutely required for the recruitment of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and for the establishment of active histone marks at the class II major histocompatibility complex transactivator (CIIta) promoter IV, whereas it is dispensable for histone acetylation at the guanylate binding protein 2 (Gbp2) promoter but required for an efficient recruitment of Pol II, which correlated with a strongly reduced, but not absent, transcriptional activity. IFNγ-induced expression of Irf7, which is mediated by STAT1 in complex with STAT2 and IRF9, did not rely on the presence of the C-terminal TAD of STAT1. Moreover, we show for the first time that the STAT1 C-terminal TAD is required for an efficient recruitment of components of the core Mediator complex to the IFN regulatory factor (Irf) 1 and Irf8 promoters, which both harbor an open chromatin state under basal conditions. Our study identified novel functions of the STAT1 C-terminal TAD in transcriptional activation and provides mechanistic explanations for the gene-specific transcriptional activity of STAT1β.
Keywords: IFNγ; IRF8; RNA polymerase II; interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1); macrophage; mediator; signal transducer and activator of transcription; transcriptional coactivator.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential regulation of Tetraodon nigroviridis Mx gene promoter activity by constitutively-active forms of STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014 May;38(1):230-43. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24680831
-
STAT2/IRF9 directs a prolonged ISGF3-like transcriptional response and antiviral activity in the absence of STAT1.Biochem J. 2015 Mar 15;466(3):511-24. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140644. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25564224 Free PMC article.
-
Type I interferon-regulated gene expression and signaling in murine mixed glial cells lacking signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 or 2 or interferon regulatory factor 9.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 7;292(14):5845-5859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756510. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28213522 Free PMC article.
-
A Positive Feedback Amplifier Circuit That Regulates Interferon (IFN)-Stimulated Gene Expression and Controls Type I and Type II IFN Responses.Front Immunol. 2018 May 28;9:1135. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01135. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29892288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of signal transducer and activator of transcription-2 in the interferon response.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012 Mar;32(3):103-10. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0099. Epub 2012 Jan 26. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012. PMID: 22280068 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Transcriptome Dynamics of In Vivo Theileria annulata Infection in Crossbred Cattle.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 22;14(9):1663. doi: 10.3390/genes14091663. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761803 Free PMC article.
-
The intrinsically disordered protein TgIST from Toxoplasma gondii inhibits STAT1 signaling by blocking cofactor recruitment.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 13;13(1):4047. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31720-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35831295 Free PMC article.
-
STAT Signature Dish: Serving Immunity with a Side of Dietary Control.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 26;15(4):487. doi: 10.3390/biom15040487. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ROS-activated CD147-type I interferon signaling axis drives vascular smooth muscle cell fate transition and abdominal aortic aneurysm progression.Redox Biol. 2025 Jul 22;86:103780. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103780. Online ahead of print. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40803247 Free PMC article.
-
STAT family of transcription factors in breast cancer: Pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities and challenges.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Nov;86(Pt 3):84-106. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.08.003. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 35995341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

