Prevalence, clinical presentations, associated risk factors and recurrence of laryngeal papillomatosis among inpatients attended at a Tertiary Hospital in Northern zone Tanzania
- PMID: 30574228
- PMCID: PMC6294976
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2018.30.209.11211
Prevalence, clinical presentations, associated risk factors and recurrence of laryngeal papillomatosis among inpatients attended at a Tertiary Hospital in Northern zone Tanzania
Abstract
Introduction: Although Laryngeal papillomatosis is a rare disease and can be conventionally managed through surgical excision as well as adjuvant therapy yet Laryngeal papillomatosis has high tendency to recur raising its prevalence in the community, airway involvement warrants dangerous complications requiring emergency tracheostomy, especially if clinical course is poorly understood and misdiagnosis is common. The study aims to determine the prevalence, clinical features, risk factors and recurrence of Laryngeal Papillomatosis among patients attending ENT department at KCMC from 2005 to 2015.
Methods: This was a 10 year experience/ Descriptive hospital based cross-sectional study conducted based on patients' medical record at KCMC. Information was recorded into data collection sheets, entered and analyzed through SPSS version 20, summarized and presented in tables and charts, proportions and percentage used to compare groups.
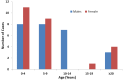
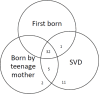
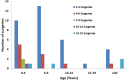
Results: 51 patients were identified over the 10 years study period corresponding to a prevalence of 0.09%. 26 were males and 25 females, ages ranging from 1 to 67 years. The median age of onset was 6 years. Children less than 5 years accounted for 19 (37.3%) and 58.8% had repeated surgeries. Clinical presentation ranged from hoarseness in 43 (84.3%) patients to weight loss 3 (5.9%) and 96.1% showed complete or partial presence of the clinical triad of risk factors.
Conclusion: Laryngeal papillomatosis is a rare disease that carries severe morbidity due to its highly recurring nature. It is primarily a paediatric disease, generally affecting more males; its clinical features highly resemble other airway obstructive diseases and therefore a careful thorough clinical evaluation is required in order to correctly diagnose Laryngeal papillomatosis.
Keywords: Laryngeal-papillomatosis; clinical; factors; features; recurrence; risk.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laryngeal papillomatosis in Senegal: A ten-year experience.Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018 Jun;135(3):221-224. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2018.01.002. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018. PMID: 29396224
-
[Laryngeal Papillomatosis: A Statistical Analysis of 60 Cases].Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 2015 Mar;118(3):192-200. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.118.192. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 2015. PMID: 26349334 Japanese.
-
[Laryngeal Papillomatosis In Niamey: Epidemiological, Diagnostic And Therapeutic Aspects].Mali Med. 2024;39(3):28-32. Mali Med. 2024. PMID: 39584640 French.
-
[Laryngeal papillomatosis: etiology, diagnostics and therapy].HNO. 2008 Dec;56(12):1190-6. doi: 10.1007/s00106-008-1711-4. HNO. 2008. PMID: 19034400 Review. German.
-
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1996 Sep;23(3):699-706. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1996. PMID: 8869953 Review.
Cited by
-
Etiology, Clinical Profile, Evaluation, and Management of Stridor in Children.Indian J Pediatr. 2021 Nov;88(11):1115-1120. doi: 10.1007/s12098-021-03722-8. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Indian J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33728566 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic diversity of HPV6 and HPV11 in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: Association with malignant transformation in the lungs and clinical outcomes.Tumour Virus Res. 2024 Dec;18:200294. doi: 10.1016/j.tvr.2024.200294. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Tumour Virus Res. 2024. PMID: 39481538 Free PMC article.
-
Photodynamic viral inactivation: Recent advances and potential applications.Appl Phys Rev. 2021 Jun;8(2):021315. doi: 10.1063/5.0044713. Appl Phys Rev. 2021. PMID: 34084253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPV and Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Brief Review.Life (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;11(11):1279. doi: 10.3390/life11111279. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An updated review of the epidemiological factors associated with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2021 Jan 28;6(2):226-233. doi: 10.1002/lio2.521. eCollection 2021 Apr. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33869755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adoga AA, Nimkur LT, Adoga AS. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis in Jos Nigeria: clinical presentation. Management and outcome. East and Central African Journal of surgery. 2007;105:105–108.
-
- Aliyu MK, Abimiku SL, Babagana MA. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: management outcome at national ear care centre. kaduna. 2010;7(2):5–7.
-
- sherif K, Nunez AD. Pappilary Thyroid carcinoma: surgical decisions. Journal of ENT masterclass. 2008;1(1):110–116.
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous