Two- versus Three-Point Internal Fixation of Displaced Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures
- PMID: 30574268
- PMCID: PMC6224286
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1604199
Two- versus Three-Point Internal Fixation of Displaced Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures
Abstract
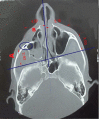
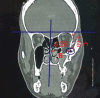
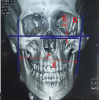
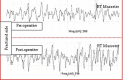
Despite the high frequency of the zygomaticomaxillary complex (ZMC) fractures, there is no consensus among facial reconstructive surgeons regarding the best surgical management; thus, surgical choice for ZMC fractures is still challenging. This study included 40 patients with displaced ZMC fracture. Twenty patients were treated with open reduction and internal fixation (OR/IF) using two-point fixation technique (at infraorbital margin and zygomaticofrontal buttress region) and the remaining 20 patients were treated with OR/IF using three-point fixation technique (at frontozygomatic suture, infraorbital margin, and zygomatico maxillary buttress). The results of both types of ZMC fractures repair were then statistically compared. No statistical differences between the two types regarding malar eminence asymmetry; projection (forward displacement) and width (medial displacement) in axial CT; inferior displacement; superior displacement and width (medial displacement) in coronal CT; angle of displacement (outward displacement) in 3D CT; masseter and temporalis muscles power electromyography; actual duration of surgery; and patient satisfaction. On the other hand, the total cost of the used plates and screws was significantly higher with three-point repair than two-point repair ( p = 0.003). Moreover, postoperative CT lateral zygoma displacement was statistically significantly better in three-point fixation. Two-point fixation modality for displaced ZMC fractures is as effective as three-point method in fixation and prevents postreduction rotation or clinical displacement with significantly lower cost.
Keywords: fracture; internal fixation; zygomaticomaxillary complex.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ansari S R, Shah S MA, Rehman B.Atta-Ur-Rehman,Pattern of zygomatic bone fractures and treatment modalities: a study Pak Oral Dent J 2010300136–40.
-
- Thiagarajan B, Narashiman S, Arjunan K. Fracture zygoma and its management our experience. Otolaryngol Online J. 2013;13:1–5.
-
- Meslemani D, Kellman R M. Zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2012;14(01):62–66. - PubMed
-
- Parasher A, Sharma R K, Makkar S. Rigid internal fixation of zygomatic fractures: a comparison of two-point and three point fixation. Indian J Plast Surg. 2007;40(01):18–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
