Serum Albumin at Start of Peritoneal Dialysis Predicts Long-Term Outcomes in Anhui Han Patients on Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 30574503
- PMCID: PMC6276754
- DOI: 10.1159/000492426
Serum Albumin at Start of Peritoneal Dialysis Predicts Long-Term Outcomes in Anhui Han Patients on Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Objective: This study assessed the relationship between serum albumin (ALB) at start of peritoneal dialysis (PD) and long-term outcomes of continuous ambulatory PD (CAPD) in Anhui Han patients.
Methods: A total of 149 Anhui Han CAPD patients were enrolled in this study and followed up for 3 years. They were initially diagnosed with the end-stage renal disease and underwent surgical PD catheter placement from January 2009 to December 2013. According to serum ALB at start of PD, the patients were divided into two groups: low ALB group (ALB < 35 g/L) and high ALB group (ALB ≥35 g/L). Demographic, hematologic, biochemical, and dialysis-related data were collected. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and log-rank test were conducted to compare patient mortality, cardiovascular mortality and technique failure between the low ALB group and the high ALB group. Cox regression analysis was performed to analyze the risk factors, calculate the hazard ratio (HR), adjusted HR (AHR) and 95% confidence interval (CI).
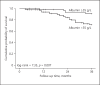
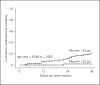
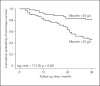
Results: The low ALB group showed a greater number of diabetes mellitus compared with the high ALB group. Patient mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and technique failure in the high ALB group were significantly lower than those in the low ALB group. In Cox regression analysis, serum ALB < 35 g/L was an independent predictor of patient mortality (AHR 3.043, 95% CI 1.085-8.536, p = 0.034), cardiovascular mortality (AHR 11.587, 95% CI 1.466-91.574, p = 0.020), and technique failure (AHR 3.148, 95% CI 1.603-6.182, p = 0.001) in CAPD patients after adjustment for sex, age, estimated glomerular filtration rate, primary renal disease, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease.
Conclusions: In Anhui Han patients on CAPD, the levels of serum ALB at start of PD are inversely correlated with patient mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and technique failure, and the long-term outcomes of patients with hypoalbuminemia at start of PD are poor. To improve the long-term outcomes of Anhui Han CAPD patients, patients with hypoalbuminemia at start of PD should be closely monitored.
Keywords: Cardiovascular mortality; Patient mortality; Peritoneal dialysis; Serum albumin; Technique failure.
Figures
References
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Harnett JD, Kent GM, Murray DC, Barre PE. Hypoalbuminemia, cardiac morbidity, and mortality in end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996;7:728–736. - PubMed
-
- Kim SB, Yang WS, Park JS. Role of hypoalbuminemia in the genesis of cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Perit Dial Int. 1999;19:S144–S149. - PubMed
-
- Cueto-Manzano AM, Quintana-Pina E, Correa-Rotter R. Long-term CAPD survival and analysis of mortality risk factors: 12-year experience of a single Mexican center. Perit Dial Int. 2001;21:148–153. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

