Limbal ischemia: Reliability of clinical assessment and implications in the management of ocular burns
- PMID: 30574887
- PMCID: PMC6324115
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_945_18
Limbal ischemia: Reliability of clinical assessment and implications in the management of ocular burns
Abstract
Purpose: Limbal ischemia is an important prognostic factor in the management of ocular burns. In this study, we evaluated the reliability of clinically assessing limbal ischemia among ophthalmic professionals.
Methods: This study included 111 ophthalmic professionals who were shown 12 diffuse illumination color slit-lamp photographs of eyes with recent chemical injuries. Respondents were asked whether the photos were assessable and if yes, then to indicate the presence, location, and grade of limbal ischemia in each case. The responses were collected using a standard data collection sheet and the inter-observer agreement was calculated.
Results: All participants responded to every question. Of the 1,332 responses, images were deemed assessable in 1,222 (91.7%) instances. The overall agreement (Fleiss' kappa) for the presence of limbal ischemia and severity of limbal ischemia was 0.106 and 0.139, respectively (P < 0.012). Among the four groups of observers, practicing cornea specialists displayed significantly (P < 0.003) higher kappa values (0.201-0.203) when compared to residents (0.131-0.185), fellows (0.086-0.127), and optometrists (0.077-0.102). All indicated a poor level of inter-rater consistency.
Conclusion: The results indicate that clinical assessment of limbal ischemia is highly subjective and there is lack of reliability even among cornea specialists who regularly manage patients with ocular burns. A non-invasive, standardized, objective, accurate, and reliable modality for ocular surface angiography is desperately needed for proper assessment and prognostication of ocular burns.
Keywords: Chemical injury; imaging; limbal ischemia; limbus; ocular burns.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

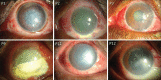
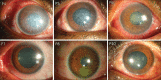
Comment in
-
Commentary: Assessment of limbal ischemia in ocular burns.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019 Jan;67(1):37. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1432_18. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30574888 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vazirani J, Nair D, Shanbhag S, Wurity S, Ranjan A, Sangwan V, et al. Limbal stem cell deficiency-demography and underlying causes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2018;188:99–103. - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Sureka SP, Shanbhag SS, Kethiri AR, Singh V, Sangwan VS, et al. Simple limbal epithelial transplantation: Long-term clinical outcomes in 125 cases of unilateral chronic ocular surface burns. Ophthalmology. 2016;123:1000–10. - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Mohamed A, Chaurasia S, Sejpal K, Vemuganti GK, Sangwan VS, et al. Clinical outcomes of penetrating keratoplasty after autologous cultivated limbal epithelial transplantation for ocular surface burns. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011;152:917–240. - PubMed
-
- Wagoner MD. Chemical injuries of the eye: Current concepts in pathophysiology and therapy. Surv Ophthalmol. 1997;41:275–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

