Effective Construction of a High-Capacity Boronic Acid Layer on a Quartz Crystal Microbalance Chip for High-Density Antibody Immobilization
- PMID: 30577674
- PMCID: PMC6339082
- DOI: 10.3390/s19010028
Effective Construction of a High-Capacity Boronic Acid Layer on a Quartz Crystal Microbalance Chip for High-Density Antibody Immobilization
Abstract
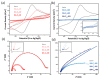
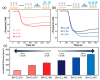
Boronic acids (BAs) provide strong potential in orientation immobilization of antibody and the modification method is crucial for efficiency optimization. A highly effective method has been developed for rapid antibody immobilization on gold electrodes through the electrodeposition of a BA⁻containing linker in this study. Aniline-based BA forms a condense layer while antibody could automatically immobilize on the surface of the electrode. Compare to traditional self-assembled monolayer method, the electrodeposition process dramatically reduces the modification time from days to seconds. It also enhances the immobilized efficiency from 95 to 408 (ng/cm²) with a strong preference being exhibited for shorter aniline-based linkers.
Keywords: boronic acid; electrodeposition; orientated antibody immobilization; quartz crystal microbalance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bengtson H.N., Homolka S., Niemann S., Reis A.J., da Silva P.E., Gerasimova Y.V., Kolpashchikov D.M., Rohde K.H. Multiplex detection of extensively drug resistant tuberculosis using binary deoxyribozyme sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017;94:176–183. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.02.051. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

