Quantitative Proteomic Profiling of Cerebrospinal Fluid to Identify Candidate Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 30578620
- PMCID: PMC6639119
- DOI: 10.1002/prca.201800105
Quantitative Proteomic Profiling of Cerebrospinal Fluid to Identify Candidate Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study is to identify the potential cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease and to evaluate these markers on independent CSF samples using parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) assays.
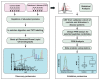
Experimental design: High-Resolution mass spectrometry and tandem mass tag (TMT) multiplexing technology are employed to identify potential biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Some of the identified potential biomarkers are validated using PRM assays.
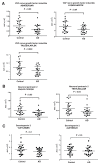
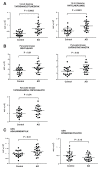
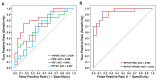
Results: A total of 2327 proteins are identified in the CSF of which 139 are observed to be significantly altered in the CSF of AD patients. The proteins altered in AD includes a number of known AD marker such as MAPT, NPTX2, VGF, GFAP, and NCAM1 as well as novel biomarkers such as PKM and YWHAG. These findings are validated in a separate set of CSF specimens from AD dementia patients and controls. NPTX2, in combination with PKM or YWHAG, leads to the best results with AUCs of 0.935 and 0.933, respectively.
Conclusions and clinical relevance: The proteins that are found to be altered in the CSF of patients with AD could be used for monitoring disease progression and therapeutic response and perhaps also for early detection once they are validated in larger studies.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; TMT; biomarker; biomedical applications; cerebrospinal fluid; mass spectrometry; parallel reaction monitoring; proteome.
© 2018 The Authors. Proteomics - Clinical Application published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MM, de Strooper B, et al. Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 2016;388:505–517. - PubMed
-
- Glenner GG, Wong CW. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;120:885–890. - PubMed
-
- Lee VM, Balin BJ, Otvos L, Jr, Trojanowski JQ. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991;251:675–678. - PubMed
-
- Lin W, Zhang J, Liu Y, Wu R, et al. Studies on diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic mechanism of Alzheimer's disease through metabolomics and hippocampal proteomics. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;105:119–126. - PubMed
-
- van Waalwijk van Doorn LJ, Gispert JD, Kuiperij HB, Claassen JA, et al. Improved Cerebrospinal Fluid-Based Discrimination between Alzheimer's Disease Patients and Controls after Correction for Ventricular Volumes. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56:543–555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

