Wave reflections and global arterial compliance during normal human pregnancy
- PMID: 30578623
- PMCID: PMC6303533
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13947
Wave reflections and global arterial compliance during normal human pregnancy
Abstract
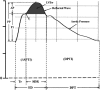
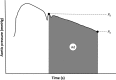
Profound changes occur in the maternal circulation during pregnancy. Routine measures of arterial function - central systolic pressure (CSP) and augmentation index (AIx) - decline during normal human pregnancy. The objectives of this study were twofold: (1) explore wave reflection indices besides CSP and AIx that are not routinely reported, if at all, during normal human pregnancy; and (2) compare wave reflection indices and global arterial compliance (gAC) obtained from carotid artery pressure waveforms (CAPW) as a surrogate for aortic pressure waveforms (AOPW) versus AOPW synthesized from radial artery pressure waveforms (RAPW) using a generalized transfer function. To our knowledge, a comparison of these two methods has not been previously evaluated in the context of pregnancy. Ten healthy women with normal singleton pregnancies were studied using applanation tonometry (SphygmoCor) at pre-conception, and then during 10-12 and 33-35 gestational weeks. CSP and AIx declined, and gAC increased during pregnancy as previously reported. As a consequence of the rise in gAC, the return of reflected waves of lesser magnitude from peripheral reflection sites to the aorta was delayed that, in turn, reduced systolic duration of reflected waves, augmentation index, central systolic pressure, LV wasted energy due to reflected waves, and increased brachial-central pulse pressure. For several wave reflection indices, those derived from CAPW as a surrogate for AOPW versus RAPW using a generalized transfer function registered greater gestational increases of arterial compliance. This discordance may reflect imprecision of the generalized transfer function for some waveform parameters, though potential divergence of carotid artery and aortic pressure waveforms during pregnancy cannot be excluded.
Keywords: Applanation tonometry; SphygmoCor; maternal cardiovascular function; pulse wave analysis; pulse wave velocity.
© 2018 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Maternal wave reflections and arterial stiffness in normal pregnancy as assessed by applanation tonometry.Hypertension. 2008 Apr;51(4):1047-51. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.106062. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Hypertension. 2008. PMID: 18259025
-
Central arterial pulse wave augmentation is greater in girls than boys, independent of height.J Hypertens. 2010 Feb;28(2):306-13. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283332286. J Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 20051902
-
Analysis of the effect of hemodialysis on peripheral and central arterial pressure waveforms.Kidney Int. 2000 Jun;57(6):2634-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00124.x. Kidney Int. 2000. PMID: 10844634
-
Clinical measurement of arterial stiffness obtained from noninvasive pressure waveforms.Am J Hypertens. 2005 Jan;18(1 Pt 2):3S-10S. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.10.009. Am J Hypertens. 2005. PMID: 15683725 Review.
-
Augmentation of the aortic and central arterial pressure waveform.Blood Press Monit. 2004 Aug;9(4):179-85. doi: 10.1097/00126097-200408000-00002. Blood Press Monit. 2004. PMID: 15311144 Review.
Cited by
-
Center-To-Periphery Arterial Stiffness Gradient Is Attenuated and/or Reversed in Pregnancy-Associated Hypertension.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Dec 24;8:766723. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.766723. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 35004884 Free PMC article.
-
A mathematical model of vascular and hemodynamics changes in early and late forms of preeclampsia.Physiol Rep. 2023 Apr;11(8):e15661. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15661. Physiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37186372 Free PMC article.
-
Second systolic peak in fetal middle cerebral artery Doppler after intrauterine transfusion.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023 Jan;307(1):241-248. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06517-0. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023. PMID: 35348831 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Cardiovascular Dysregulation During Early Pregnancy After In Vitro Fertilization Cycles in the Absence of a Corpus Luteum.Hypertension. 2019 Sep;74(3):705-715. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13015. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31352818 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical remodeling of the murine descending thoracic aorta during late-gestation pregnancy.Curr Res Physiol. 2023 Jul 18;6:100102. doi: 10.1016/j.crphys.2023.100102. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37575979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chemla, D. , Hebert J. L., Coirault C., Zamani K., Suard I., Colin P., et al. 1998. Total arterial compliance estimated by stroke volume‐to‐aortic pulse pressure ratio in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 274:H500–H505. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. H. , Ting C. T., Nussbacher A., Nevo E., Kass D. A., Pak P., et al. 1996. Validation of carotid artery tonometry as a means of estimating augmentation index of ascending aortic pressure. Hypertension 27:168–175. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, H. M. , Park S., Huang Q., Hoshide S., Wang J. G., Kario K., et al. ; Characteristics on the Management of Hypertension in Asia ‐ Morning Hypertension Discussion G . 2017. Vascular aging and hypertension: implications for the clinical application of central blood pressure. Int. J. Cardiol. 230:209–213. - PubMed
-
- Conrad, K. P. , Debrah D. O., Novak J., Danielson L. A., and Shroff S. G.. 2004. Relaxin modifies systemic arterial resistance and compliance in conscious, nonpregnant rats. Endocrinology 145:3289–3296. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

