An N6-methyladenosine at the transited codon 273 of p53 pre-mRNA promotes the expression of R273H mutant protein and drug resistance of cancer cells
- PMID: 30578766
- PMCID: PMC6407121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.12.014
An N6-methyladenosine at the transited codon 273 of p53 pre-mRNA promotes the expression of R273H mutant protein and drug resistance of cancer cells
Abstract
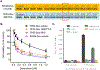
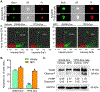
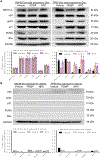
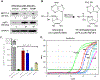
Mutant p53 proteins that promote cancer cell invasive growth, metastasis and drug resistance emerge as therapeutic targets. Previously, we reported that suppression of ceramide glycosylation restored wild-type p53 protein and tumor suppressing function in cancer cells heterozygously carrying p53 R273H, a hot-spot missense mutation; however, the mechanisms underlying the control of mutant protein expression remain elusive. Herein, we report that an N6-methyladenosine (m6A) at the point-mutated codon 273 (G > A) of p53 pre-mRNA determines the mutant protein expression. Methylation of the transited adenosine was catalyzed by methyltransferase like 3 (METTL3), and this m6A-RNA promoted a preferential pre-mRNA splicing; consequently, the produced p53 R273H mutant protein resulted in acquired multidrug resistance in colon cancer cells. Furthermore, glycosphingolipids (particularly globotriaosylceramide) generated from serial ceramide glycosylation were seen to activate cSrc and β-catenin signaling so as to upregulate METTL3 expression, in turn promoting expression of p53 R273H mutant protein, with consequent drug resistance. Conversely, either silencing METTL3 expression by using small interfering RNA (siRNA) or inhibiting RNA methylation with neplanocin A suppressed m6A formation in p53 pre-mRNA, and substantially increased the level of phosphorylated p53 protein (Ser15) and its function in cells heterozygously carrying the R273H mutation, thereby re-sensitizing these cells to anticancer drugs. Concordantly, suppression of ceramide glycosylation repressed METTL3 expression and m6A formation in p53 pre-mRNA, thus sensitizing cells carrying R273H to anticancer drugs. This study uncovers a novel function of pre-mRNA m6A as a determinant of mutant protein expression in cancer cells heterozygously carrying the TP53 R273H mutation. Suppressing both RNA methylation and ceramide glycosylation might constitute an efficacious and specific approach for targeting TP53 missense mutations coding for a G > A transition, thereby improving cancer treatments.
Keywords: Drug resistance; Glucosylceramide synthase; Missense mutation; N(6)-methyladenosine; RNA methylation; Tumor suppressor p53.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclose statement
Authors claim no competing financial interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of glucosylceramide synthase eliminates the oncogenic function of p53 R273H mutant in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and induced pluripotency of colon cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):60575-60592. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11169. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27517620 Free PMC article.
-
Gb3-cSrc complex in glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains contributes to the expression of p53 mutant protein and cancer drug resistance via β-catenin-activated RNA methylation.FASEB Bioadv. 2020 Sep 2;2(11):653-667. doi: 10.1096/fba.2020-00044. eCollection 2020 Nov. FASEB Bioadv. 2020. PMID: 33205006 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant p53-R273H mediates cancer cell survival and anoikis resistance through AKT-dependent suppression of BCL2-modifying factor (BMF).Cell Death Dis. 2015 Jul 16;6(7):e1826. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.191. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26181206 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant p53 in colon cancer.J Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Apr 1;11(4):267-276. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy075. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30496442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of METTL3 in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic targeting.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Aug 27;13(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00951-w. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32854717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N6 -methyladenosine-RNA methylation promotes expression of solute carrier family 7 member 11, an uptake transporter of cystine for lipid reactive oxygen species scavenger glutathione synthesis, leading to hepatoblastoma ferroptosis resistance.Clin Transl Med. 2022 May;12(5):e889. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.889. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35604883 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Caffeic Acid Attenuates Multi-Drug Resistance in Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Efflux Function of Human P-glycoprotein.Molecules. 2020 Jan 7;25(2):247. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020247. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31936160 Free PMC article.
-
Function and clinical significance of N6-methyladenosine in digestive system tumours.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jul 10;10(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s40164-021-00234-1. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34246319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of recurrent somatic mutations that alter conserved m6A motifs in human cancer.NAR Cancer. 2025 Apr 23;7(2):zcaf014. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcaf014. eCollection 2025 Jun. NAR Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40271220 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the epitranscriptome: a new frontier for cancer therapy and drug resistance.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 21;22(1):513. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01854-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39434167 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

