Fibrostenotic eosinophilic esophagitis might reflect epithelial lysyl oxidase induction by fibroblast-derived TNF-α
- PMID: 30578874
- PMCID: PMC6586527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.067
Fibrostenotic eosinophilic esophagitis might reflect epithelial lysyl oxidase induction by fibroblast-derived TNF-α
Abstract
Background: Fibrosis and stricture are major comorbidities in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Lysyl oxidase (LOX), a collagen cross-linking enzyme, has not been investigated in the context of EoE.
Objective: We investigated regulation of epithelial LOX expression as a novel biomarker and functional effector of fibrostenotic disease conditions associated with EoE.
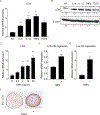
Methods: LOX expression was analyzed by using RNA-sequencing, PCR assays, and immunostaining in patients with EoE; cytokine-stimulated esophageal 3-dimensional organoids; and fibroblast-epithelial cell coculture, the latter coupled with fluorescence-activated cell sorting.
Results: Gene ontology and pathway analyses linked TNF-α and LOX expression in patients with EoE, which was validated in independent sets of patients with fibrostenotic conditions. TNF-α-mediated epithelial LOX upregulation was recapitulated in 3-dimensional organoids and coculture experiments. We find that fibroblast-derived TNF-α stimulates epithelial LOX expression through activation of nuclear factor κB and TGF-β-mediated signaling. In patients receiver operating characteristic analyses suggested that LOX upregulation indicates disease complications and fibrostenotic conditions in patients with EoE.
Conclusions: There is a novel positive feedback mechanism in epithelial LOX induction through fibroblast-derived TNF-α secretion. Esophageal epithelial LOX might have a role in the development of fibrosis with substantial translational implications.
Keywords: Eosinophilic esophagitis; TGF-β; TNF-α; coculture; fibrosis; lysyl oxidase.
Copyright © 2018 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

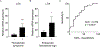



Comment in
-
Bagels and LOX in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Jul;144(1):41-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.03.034. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31051184 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cheng E, Zhang X, Wilson KS, Wang DH, Park JY, Huo X, et al. JAK-STAT6 Pathway Inhibitors Block Eotaxin-3 Secretion by Epithelial Cells and Fibroblasts from Esophageal Eosinophilia Patients: Promising Agents to Improve Inflammation and Prevent Fibrosis in EoE. PLoS ONE 2016;11:e0157376. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 DK103953/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK118310/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK118304/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI117804/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA098101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK106444/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK100088/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001879/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114436/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA174176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK121159/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

