Quantification of morphometry and intensity features of intracranial arteries from 3D TOF MRA using the intracranial artery feature extraction (iCafe): A reproducibility study
- PMID: 30580079
- PMCID: PMC6469503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.12.007
Quantification of morphometry and intensity features of intracranial arteries from 3D TOF MRA using the intracranial artery feature extraction (iCafe): A reproducibility study
Abstract
Background: Accurate and reliable vascular features extracted from 3D time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) can help evaluate cerebral vascular diseases and conditions. The goal of this study was to evaluate the reproducibility of an intracranial artery feature extraction (iCafe) algorithm for quantitative analysis of intracranial arteries from TOF MRA.
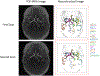
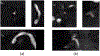
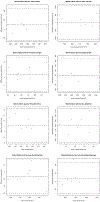
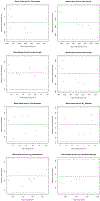
Methods: Twenty-four patients with known intracranial artery stenosis were recruited and underwent two separate MRA scans within 2 weeks of each other. Each dataset was blinded to associated imaging and clinical data and then processed independently using iCafe. Inter-scan reproducibility analysis was performed on the 24 pairs of scans while intra-/inter-operator reproducibility and stenosis detection were assessed on 8 individual MRA scans. After tracing the vessels visualized on TOF MRA, iCafe was used to automatically extract the locations with stenosis and eight other vascular features. The vascular features included the following six morphometry and two signal intensity features: artery length (total, distal, and proximal), volume, number of branches, average radius of the M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery, and average normalized intensity of all arteries and large vertical arteries. A neuroradiologist independently reviewed the images to identify locations of stenosis for the reference standard. Reproducibility of stenosis detection and vascular features was assessed using Cohen's kappa, the intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC), and within-subject coefficient of variation (CV).
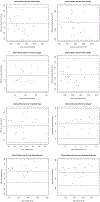
Results: The segment-based sensitivity of iCafe for stenosis detection ranged from 83.3-91.7% while specificity was 97.4%. Kappa values for inter-scan and intra-operator reproducibility were 0.73 and 0.77, respectively. All vascular features demonstrated excellent inter-scan and intra-operator reproducibility (ICC = 0.91-1.00, and CV = 1.21-8.78% for all markers), and good to excellent inter-operator reproducibility (ICC = 0.76-0.99, and CV = 3.27-15.79% for all markers).
Conclusion: Intracranial artery features can be reliably quantified from TOF MRA using iCafe to provide both clinical diagnostic assistance and facilitate future investigative quantitative analyses.
Keywords: Feature measurement; Intracranial artery; Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA); Reproducibility; Stenosis detection.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
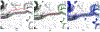
References
-
- Caplan LR, Gorelick PB, Hier DB. Race, sex and occlusive cerebrovascular disease: a review. Stroke. 1986;17:648–55. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2197–223. - PubMed
-
- Qureshi AI, Feldmann E, Gomez CR, Johnston SC, Kasner SE, Quick DC, et al. Intracranial atherosclerotic disease: An update. Ann Neurol. 2009;66:730–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

