Clinical Features and Prognostic Factors in Elderly Ewing Sarcoma Patients
- PMID: 30580374
- PMCID: PMC6320658
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.911882
Clinical Features and Prognostic Factors in Elderly Ewing Sarcoma Patients
Abstract
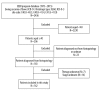
BACKGROUND Elderly patients with Ewing sarcoma have a very poor prognosis, and treatment remains a challenge. However, the outcomes and potential prognostic factors of elderly Ewing sarcoma patients are rarely documented. Therefore, we investigated the prognosis of this special cohort and determine independent prognostic factors. MATERIAL AND METHODS A cohort of Ewing sarcoma patients aged over 40 years from 1973 to 2015 was identified from the National Cancer Institute's Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. The Kaplan-Meier method and a Cox proportional hazard regression model were used for the prognostic analysis. RESULTS A total of 162 patients were included with a mean age of 53 years. The 5-year overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) rates of the entire group were 43.7% and 47.9%, respectively. The sex, location, tumor size, and radiation treatment had no effect on survival outcomes on univariate analysis. Tumor stage, surgery, and chemotherapy were significant indicators of both OS and CSS on multivariable analysis. CONCLUSIONS Surgery in combination with chemotherapy had a significant survival benefit in elderly Ewing sarcoma patients and should be recommended.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Maheshwari AV, Cheng EY. Ewing sarcoma family of tumors. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18:94–107. - PubMed
-
- Dunst J, Schuck A. Role of radiotherapy in Ewing tumors. Pediatric Blood Cancer. 2004;42:465–70. - PubMed
-
- Duchman KR, Gao Y, Miller BJ. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with Ewing’s sarcoma using the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) program database. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015;39:189–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

