Epac1 deacetylates HMGB1 through increased IGFBP-3 and SIRT1 levels in the retinal vasculature
- PMID: 30581279
- PMCID: PMC6279194
Epac1 deacetylates HMGB1 through increased IGFBP-3 and SIRT1 levels in the retinal vasculature
Abstract
Purpose: Inflammation is a key component of retinal disease. We previously reported that exchange protein for cAMP 1 (Epac1) reduced inflammatory mediators, including total levels of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in retinal endothelial cells (RECs) and the mouse retina. The goal of this study was to determine intermediate pathways that allow Epac1 to reduce HMGB1, which could lead to novel targets for therapeutics.
Methods: We used endothelial cell-specific conditional knockout mice for Epac1 and RECs to investigate whether Epac1 requires activation of insulin like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) to reduce acetylated HMGB1 levels with immunoprecipitation, western blot, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
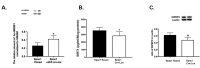
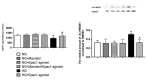
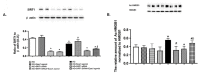
Results: Data showed that high glucose reduced IGFBP-3 and SIRT1 levels, and increased acetylation of HMGB1 in RECs. An Epac1 agonist reduced acetylated HMGB1 levels in high glucose. The Epac1 agonist could not reduce HMGB1 or SIRT1 levels when IGFBP-3 siRNA was used. The agonist also could not reduce HMGB1 when SIRT1 siRNA was used. The mouse retina showed that loss of Epac1 increases acetylated HMGB1 levels and reduces IGFBP-3 and SIRT1 levels.
Conclusions: Taken together, the data suggest that Epac1 activates IGFBP-3 to increase SIRT1, leading to a significant reduction in acetylated HMGB1. These findings provide novel therapeutic targets for reducing key inflammatory cascades in the retina.
Figures
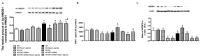
Similar articles
-
Epac1 Requires AMPK Phosphorylation to Regulate HMGB1 in the Retinal Vasculature.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Sep 1;61(11):33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.11.33. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32940662 Free PMC article.
-
PKA regulates HMGB1 through activation of IGFBP-3 and SIRT1 in human retinal endothelial cells cultured in high glucose.Inflamm Res. 2018 Dec;67(11-12):1013-1019. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1196-x. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 30328477 Free PMC article.
-
Epac1 Blocks NLRP3 Inflammasome to Reduce IL-1β in Retinal Endothelial Cells and Mouse Retinal Vasculature.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:2860956. doi: 10.1155/2017/2860956. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28348460 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the inflammatory response of vascular endothelial cells by EPAC1.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(2):434-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01808.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22145651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential of a Novel Class of EPAC-Selective Agonists to Combat Cardiovascular Inflammation.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2017 Dec 5;4(4):22. doi: 10.3390/jcdd4040022. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2017. PMID: 29367551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epac1 Requires AMPK Phosphorylation to Regulate HMGB1 in the Retinal Vasculature.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Sep 1;61(11):33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.11.33. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32940662 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 regulates inflammatory mediators in retinal endothelial cells.Mol Vis. 2024 Oct 5;30:298-303. eCollection 2024. Mol Vis. 2024. PMID: 39959177 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
TNFAIP3 may be key to TLR4-activation of the inflammasome in the retinal vasculature.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Jul;220:109108. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109108. Epub 2022 May 11. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 35568203 Free PMC article.
-
The SIRT1-HMGB1 axis: Therapeutic potential to ameliorate inflammatory responses and tumor occurrence.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 19;10:986511. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.986511. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36081910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of High Mobility Group Box 1 in Cardiovascular Diseases.Inflammation. 2022 Oct;45(5):1864-1874. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01668-3. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Inflammation. 2022. PMID: 35386038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kassel KM, Wyatt TA, Panettieri RA, Jr, Toews ML. Inhibition of human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation by beta 2-adrenergic receptors and cAMP is PKA independent: evidence for EPAC involvement. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008;294:L131–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

